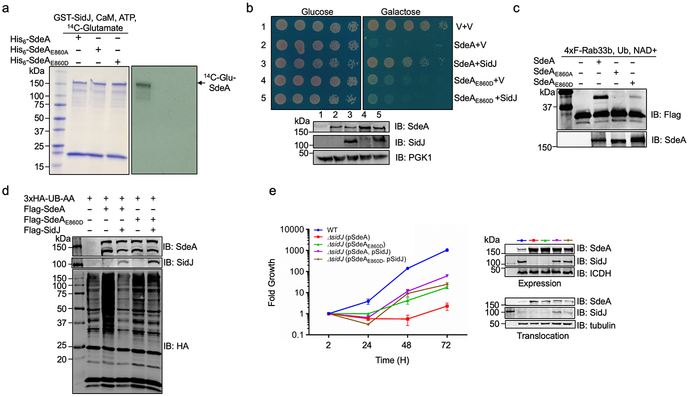
Extended data Fig. 9. SidJ functions to regulate the activity of SdeA during L. pneumophila infection.
a. SdeAE860D is resistant to glutamylation catalyzed by SidJ. SdeA, SdeAE860A or SdeAE860D was added to reactions containing GST-SidJ, 14C-glutamate ATP and CaM and the reactions were allowed to proceed for 2 h at 37°C. After separation by SDS-PAGE, the incorporation of 14C-glutamate was detected by autoradiography.
b. Yeast toxicity induced by SdeAE860D cannot be suppressed by SidJ. A plasmid that directs the expression of SidJ was introduced into yeast strains expressing SdeA or SdeAE860D from a galactose inducible promoter, serially diluted yeast cells were spotted onto glucose or galactose medium for 2 d and the growth of the cells was evaluated by imaging (upper panels). The expression of SidJ, SdeA and SdeAE860D was determined by immunoblotting with specific antibodies. The PGK1 (3-phosphoglyceric phosphokinase-1) was probed as a loading control (lower panels).
c. SdeAE860D still ubiquitinates Rab33b. Reactions containing the indicated components were allowed to proceed for 2 h at 37°C, samples were then resolved by SDS-PAGE and ubiquitination of Rab33b was probed by immunoblotting with a Flag-specific antibody to detect the production of modified Rab33b with a higher molecular weight.
d. SdeAE860D-mediated protein ubiquitination in mammalian cells is insensitive to SidJ. HEK293T cells were transfected to express the indicated proteins for 16-18 h. Cleared cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with an HA specific antibody to detected proteins ubiquitinated by 3xHA-Ub-AA. The levels of SdeA, SdeAE860D and SidJ were assessed by antibodies specific for these proteins. Note that coexpression of SidJ reduced the ubiquitination induced by SdeA but not SdeAE860D. In panels a-d, data shown were one representative from at least three independent experiments that had similar results.
e. The effects of SidJ on intracellular growth defect caused by overexpression of SdeA or SdeAE860D. The indicated L. pneumophila strains were used to infect Acanthamoeba castellanii at an MOI of 0.05 and the growth of the bacteria was evaluated at 24 h intervals. Fold growth was calculated based on total bacterial counts at the indicated time points. Note that the difference between strain ∆sidJ (pSdeA) and ∆sidJ (pSdeA, pSidJ). The growth defect caused by overexpressing the SdeAE860D mutant cannot be rescued by SidJ. The levels of relevant proteins in bacterial cells and in infected cells were probed by immunoblotting from total bacterial cell lysates and the saponin-soluble fraction of infected cells, with ICDH and tubulin as loading controls, respectively (right panels). Results showen are from one representative experiment done in triplicate from three independent experiments; error bars represent s.e.m. (n = 3).