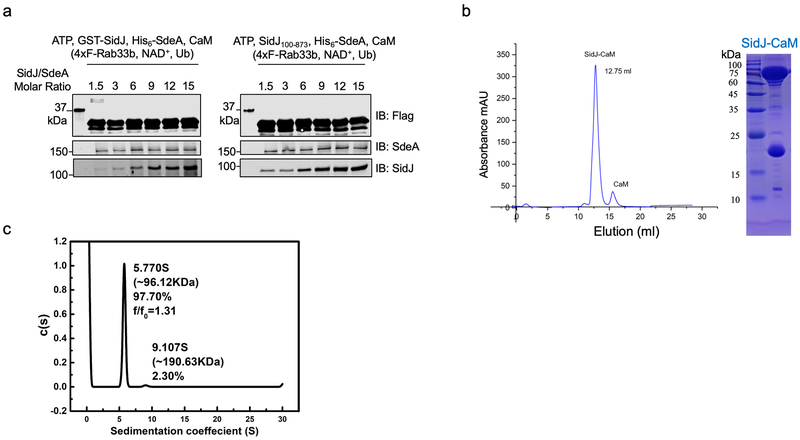
Extended Data Fig. 4. SidJ forms stable heterodimer with CaM at the molar ratio of 1:1.
a. SidJ∆N99 maintains the ability to inhibit SdeA activity at levels comparable to full-length SidJ. SdeA was incubated with GST-SidJ or SidJ∆N99 at indicated molar ratios in reactions containing ATP, L-Glu, CaM for 2 h at 37°C. A cocktail containing 4xFlag-Rab33b, NAD+, and ubiquitin was added to each reaction for additional 2 h at 37°C, proteins resolved by SDS-PAGE were probed with the indicated antibodies. SdeA activity was measured by the production of ubiquitinated Rab33b as indicated by a shift in molecular weight.
b. Size exclusion chromatography profiles of SidJ-CaM. Purified proteins were separated by a Superdex 200 increase 10/300 column (GE Healthcare) on an AKTA pure system (left). Fractions with strong absorbance at OD260 were collected and analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by detection with Coomassie brilliant blue staining (right).
c. The heterodimer formed between SidJ∆N99 with CaM is a monomer. Analytical ultracentrifugation analysis yielded a sedimentation coefficient of 5.770 S, and a molecular mass of approximately 96.12 kDa, indicating the heterodimer of SidJ∆N99 and CaM. In each panel, data shown were one representative from at least three independent experiments that had similar results.