Table 1. Photophysical properties of ASiPa and NIR-ASiPa analogues.
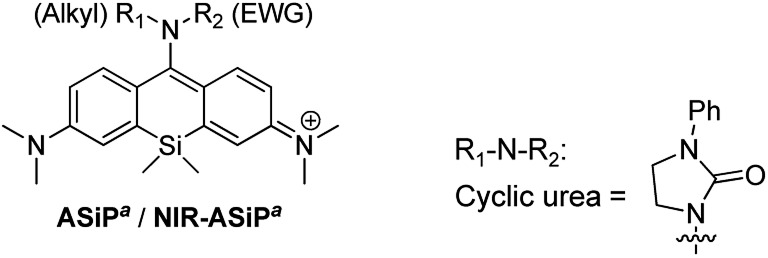
| |||||
| R 1 (alkyl) | R 2 (EWG) | λ abs a /nm | λ em b /nm | Φ F c | |
| ASiPa1 | Me | H | 452 | 612 | 0.33 d |
| ASiPa2 | Bn | H | 469 | 623 | 0.34 e |
| ASiPa3 | Propargyl | H | 473 | 628 | 0.25 e |
| NIR-ASiPa1 | Me | CO2Bn | 669 | 685 | 0.42 f |
| NIR-ASiPa2 | Propargyl | COCH3 | 676 | 694 | 0.31 e |
| NIR-ASiPa3 | Propargyl | COCF3 | 684 | 707 | 0.27 e |
| NIR-ASiPa4 | Propargyl | SO2CF3 | 694 | 713 | 0.25 e |
| NIR-ASiPa5 | Bn | COCF3 | 684 | 704 | 0.29 e |
| NIR-ASiPa6 | Cyclic urea | 674 | 690 | 0.22 e | |
aMaximum absorption wavelength.
bMaximum emission wavelength in PBS (pH 7.4).
cFluorescence quantum yield.
dDetermined in methanol using fluorescein as the reference (ΦF = 0.95 in 0.1 M NaOH).18
eDetermined in ethanol using rhodamine 101 (ΦF = 0.915 in EtOH) as the reference dye.
fDetermined in CH3CN using Nile blue (ΦF = 0.27 in ethanol) as the reference dye.
