Figure 1.
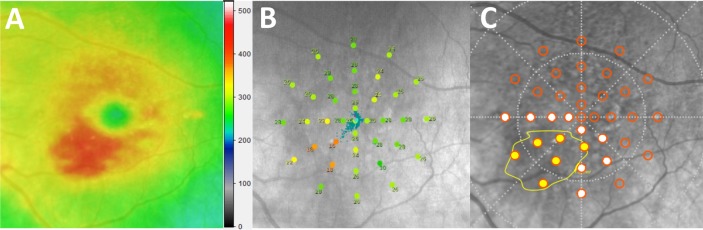
(A) Retinal thickness heat map generated by the Eye Explorer software (Heidelberg Engineering) demonstrating an area of elevation (red) secondary to retinal fluid at the inferior nasal retina of a left eye. False-color scale bar shows retinal thickness (μm). (B) NIR scout image with overlaid retinal sensitivity results from the MAIA. The AMD 6° grid is colored to denote varying threshold measurement values (dB) showing the area of low sensitivity is associated with retinal fluid. (C) Relationship between the fluid location (yellow boundary) and the location of the sensitivity testing (orange circles). Points falling within or on the area demarcated by the yellow boundary were classified as co-located with fluid (yellow-filled test points), those immediately surrounding were classified as perifluid (white-filled test points) and those further removed were classified as peripheral to fluid.