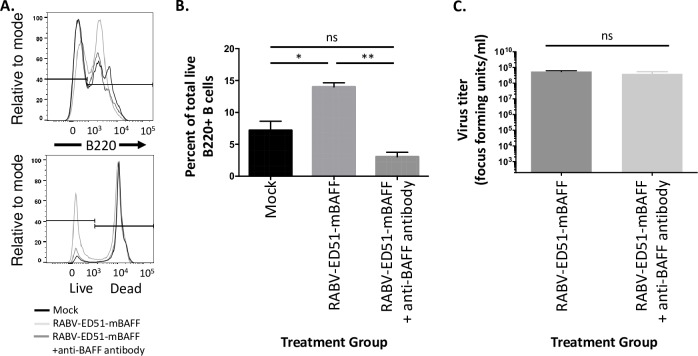
Fig 4. Virus membrane-anchored ED51-mBAFF is functional.
Naïve primary murine splenocytes were infected with a MOI of 5 with sucrose-purified RABV, RABV-ED51-mBAFF, or RABV-ED51-mBAFF pre-treated with a neutralizing anti-BAFF antibody. Splenocytes treated with media alone (mock-infected) served as a negative control. No additional mitogens were added to the culture to maintain the B cells and accessory splenocytes in a resting state similar to that in which they would exist in-vivo at the time of initial immunization. Two days later, cells were collected and analyzed for B cell survival by staining cells with anti-B220-PE antibody and Fixable Live/Dead-DAPI stain followed by FACS analyses. (A) Gating strategy for the presence of live B220+ cells. (B) Summary graph showing the percent of live B220+ cells. (C) BSR cells (a derivative of baby hamster kidney cells) were infected with a MOI of 5 with sucrose-purified RABV-ED51-mBAFF or RABV-ED51-mBAFF pre-treated with a neutralizing anti-BAFF antibody. Two days later, supernatants were collected and titered on BSR cells. To compare two groups of data, an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test was used (*p≤0.05; **p≤0.01; ns = not significant; N = 2 completed in duplicate).