Figure 8.
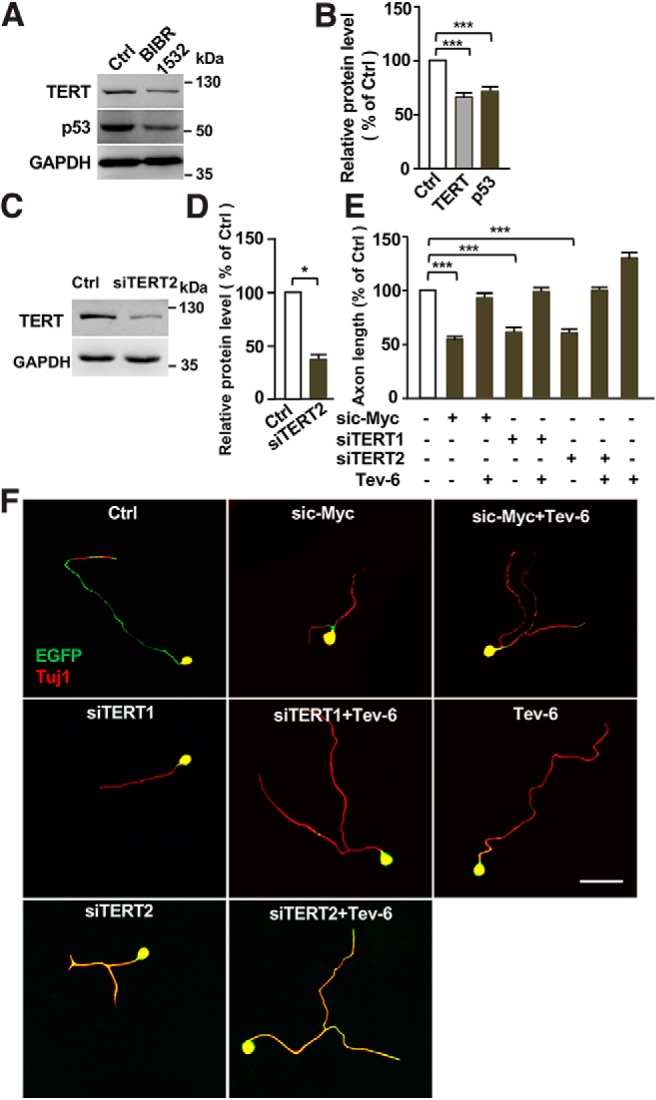
p53 acts downstream of c-Myc and TERT to regulate regenerative sensory axon growth. A, Representative Western blot images showing that inhibition of TERT activity with its specific inhibitor BIBR1532 led to reduced levels of TERT and p53 in sensory neurons. B, Quantification of the Western blot results shown in A from three independent experiments. p = 0.0001 for TERT vs control, p = 0.0002 for p53 vs control. C, Representative Western blot images showing that a different siRNA against TERT (siTERT2) resulted in reduced level of TERT in sensory neurons. D, Quantification of the Western blot results shown in C from three independent experiments. p = 0.0114. E, Quantification of the average axon lengths in F from three independent experiments. p = 0.0007 for sic-Myc vs control, p = 0.0009 for siTERT1 vs control, p = 0.0008 for siTERT2 vs control. F, Representative images showing that activation of p53 activity with tenovin-6 (0.5 μm) restored sensory axon regeneration defects induced by knocking down c-Myc with sic-Myc or TERT with two different siRNAs (siTERT1, siTERT2). Scale bar, 50 μm. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001.
