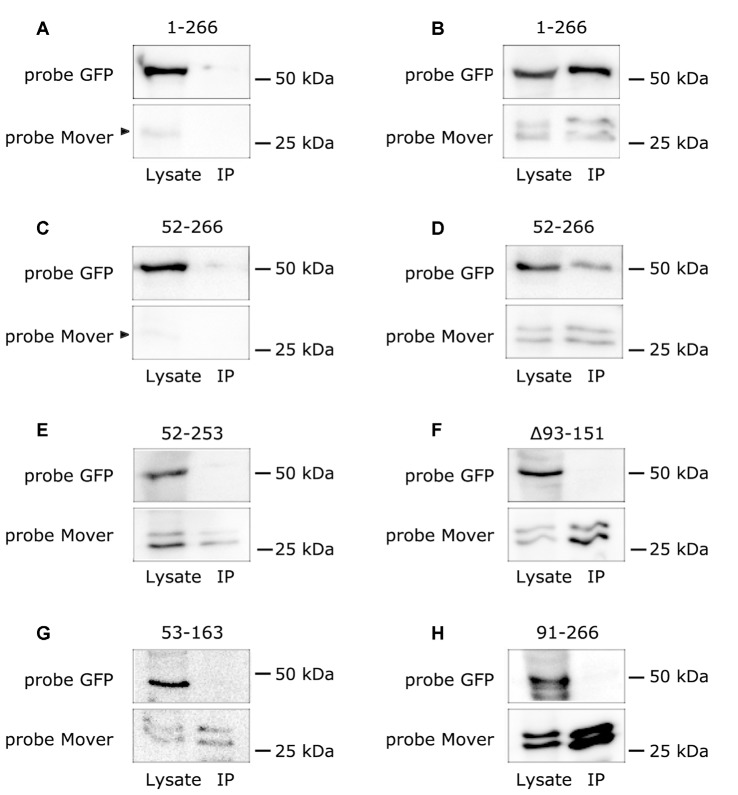
Figure 2.
Mover variants that fail to target fail to undergo homomeric interaction with full-length Mover. The figure shows Western blots analyzing the results of immunoprecipitation of Mover variants expressed in HEK293 cells. (A–H) Each GFP-tagged Mover variant (indicated on top of each panel) was separately co-expressed with myc-tagged Mover. Sepharose-coupled antibodies against the myc epitope were used to pull down protein complexes. The 30 kDa region of the blot was probed with anti-Mover, to verify immunoprecipitation of Mover-myc, which runs as a double band. Panels (A,C) are controls where the GFP-tagged constructs were expressed without Mover-myc, showing that the GFP tagged constructs expressing amino acids 1-266 and 52-266 display only residual binding to Sepharose beads. The arrowheads indicate degradation products of the GFP-Mover constructs detected by the Mover antibody. “Lysate” indicates samples obtained before adding anti-myc antibodies, “IP” indicates samples of the immunoprecipitation pellet. The regions of the blot corresponding to the molecular weights of the GFP-tagged proteins were probed with anti-GFP. Only full-length Mover-mGFP (“1-266”) and the variant lacking the amino terminal 51 amino acids (“52-266”) co-immunoprecipitate with Mover-myc. All others fail to co-immunoprecipitate. The data represent two independent experiments, i.e., two HEK293 cell transfections followed by lysis and co-immunoprecipitation.