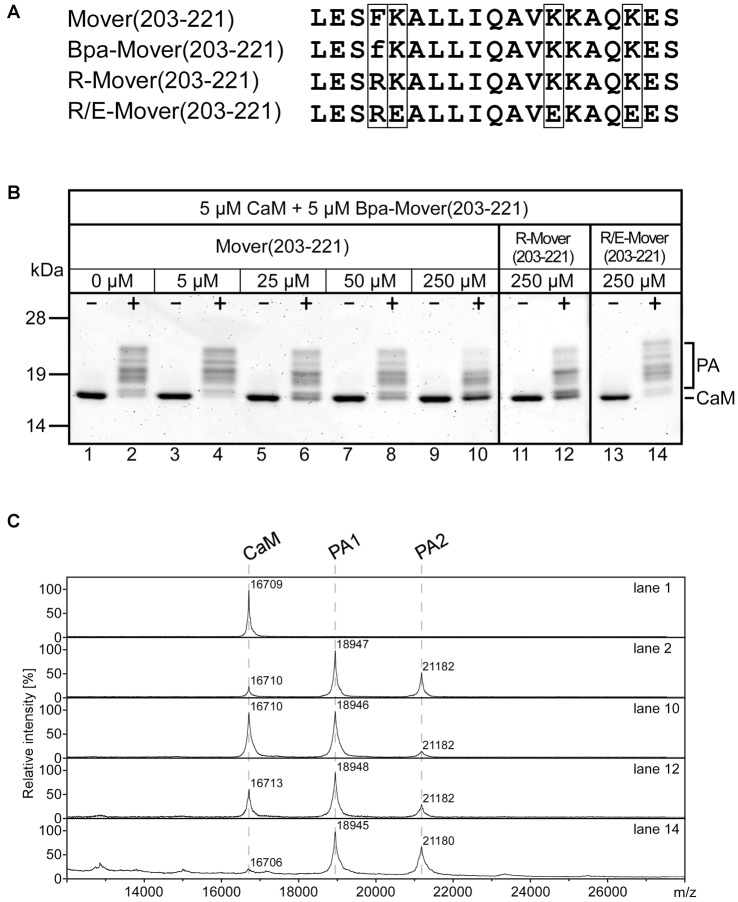
Figure 4.
CaM-binding properties of wildtype (WT) and mutated Mover peptides. (A) Amino acid sequences of Mover(203-221), the photoreactive variant Bpa-Mover(203-221), the point mutant R-Mover(203-221) carrying an Arg residue instead of the hydrophobic anchor residue Phe, and the CaM-binding deficient R/E-Mover(203-221) carrying multiple mutations of basic residues within the CaM-binding sequence in addition. The sequence positions for amino acid exchanges are boxed. f, p-benzoylphenylalanine (Bpa). For photoaffinity labeling (PAL)-based competition assays, 5 μM CaM was incubated with 5 μM Bpa-Mover(203-221). Photoreactions were analyzed by gel electrophoresis (B) and MALDI-TOF-MS (C) to monitor the formation of covalent photoadducts (PA) in the mass range of 19 kDa (PA1, 1:1 peptide/CaM complex) to 21 kDa (PA2, 2:1 peptide/CaM complex). Photoreactions were performed in the absence (−) and presence (+) of 100 μM Ca2+, and with increasing concentrations of Mover(203-221), R-Mover(203-221), and R/E-Mover(203-221) as competitors. For the mutant peptides, only the highest concentration [50-fold molar excess over Bpa-Mover(203-221)] is shown. As can be followed most clearly by means of the intensity of the signal for free CaM, Mover(203-221) effectively suppressed photoadduct formation, while the mutant competitors R-Mover(203-221) and R/E-Mover(203-221) showed reduced or no affinity to CaM, respectively. Note that also a 50-fold molar excess of Mover(203-221) did not lead to full suppression of photoadduct formation. This was most likely due to the known positive correlation between bulkiness/hydrophobicity of N-terminal anchor positions in amphipathic CaM-binding peptides and their affinity for CaM (O’Neill et al., 1989; Dimova et al., 2006). Accordingly, Bpa-Mover(203-221) with a Bpa anchor residue (two phenyl moieties) binds CaM with a higher affinity than Mover(203-221) with a Phe anchor residue (one phenyl moiety). Two independent experiments were performed.