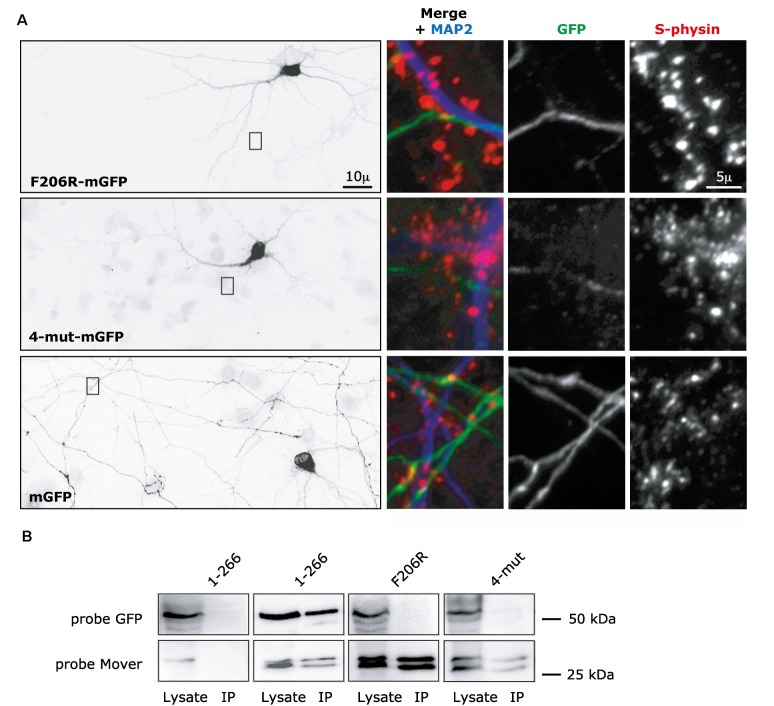
Figure 6.
Targeting and self-interaction properties of Mover constructs containing mutations in the CaM binding domain. (A) F206R-mGFP, corresponding to full-length Mover carrying one point mutation, and 4-mut-mGFP, corresponding to full-length Mover carrying four point mutations (F206R, K207E, K215E and K219E) are diffusely distributed in rat cultured hippocampal neurons. Their distribution resembled that of soluble mGFP alone. The overviews (left) show inverted gray level epifluorescence images of GFP-immunofluorescence. The zooms on the right represent triple-fluorescence images of the boxes, showing that axonal areas (MAP2 negative processes) of the transfected neurons do not contain local accumulation of the constructs even where the axon contacts a dendrite (MAP2 positive process), i.e., at a location where synapses can be formed. Synaptophysin (S-physin) is a marker for presynaptic SV clusters. The distribution of each construct was analyzed in more than 30 neurons from three independent experiments. (B) Full-length Mover (1-266) co-immunoprecipitates with Mover-myc in transfected HEK293 cells, but the F206R mutant and the 4-mut mutant do not, indicating that these point mutations disrupt homomeric interaction of Mover. The data represent two independent experiments, i.e., two HEK293 cell transfections followed by lysis and co-immunoprecipitation.