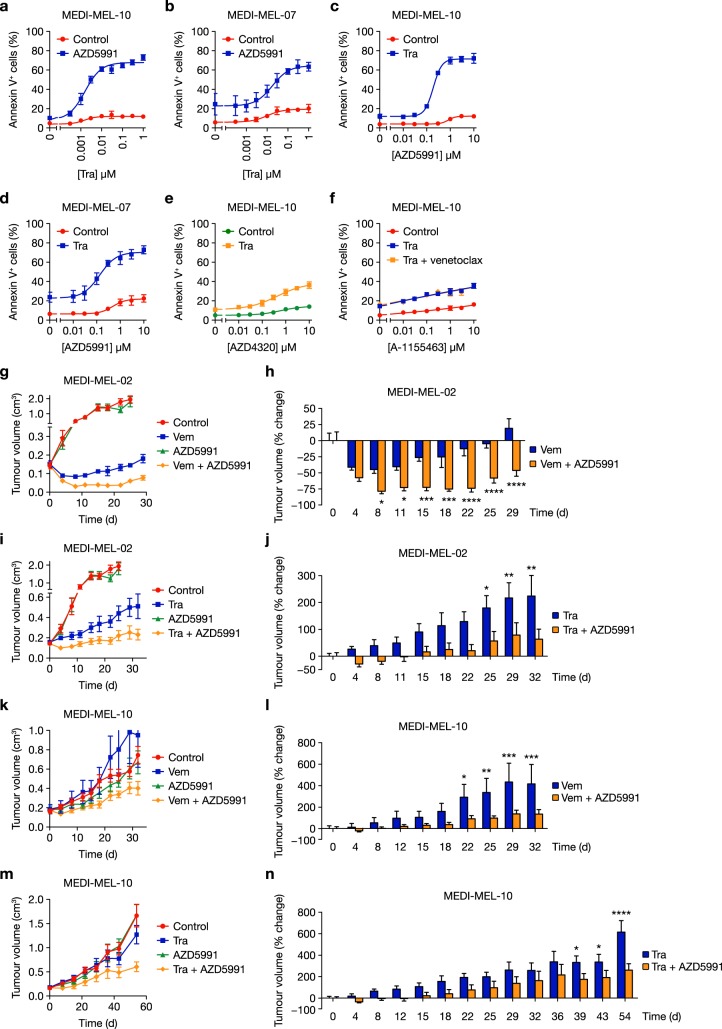
Fig. 4.
BRAFi or MEKi combine with AZD5991 to inhibit growth of patient-derived xenografts. a, b MEDI-MEL-10 (a) and MEDI-MEL-07 (b) PDX cell lines were treated with increasing concentrations of trametinib (Tra) with or without 1 μM AZD5991 for 72 h. c, d MEDI-MEL-10 (c) or MEDI-MEL-07 (d) cells were treated with increasing concentrations of AZD5991 with or without 0.3 μM trametinib (Tra) for 72 h. e MEDI-MEL-10 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of AZD4320 with or without 0.3 μM trametinib (Tra) for 72 h. f MEDI-MEL-10 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of A-1155463 with or without 0.3 μM trametinib (Tra) and 3 μM venetoclax for 72 h. a–f Apoptosis was assessed by Annexin V positivity using flow cytometry. Results are mean ± SD of three or more independent experiments. g–n NOD SCID mice were implanted subcutaneously with MEDI-MEL-02 (g–j) or MEDI-MEL-10 (k–n) tumour pieces. Upon reaching 0.15–0.2 cm3 mice were randomised by tumour volume and body mass for dosing (n = 10 per group for MEDI-MEL-02, n = 9 per group for MEDI-MEL-10) with vehicle-only (Control), 20 mg kg−1 vemurafenib (Vem) twice daily with an 8 h interval, 1 mg kg−1 trametinib (Tra) daily, and/or 60 mg kg−1 AZD5991 three times per week, as indicated. Mice were dosed on these schedules throughout the duration of the experiment, except in m and n for which dosing ceased after day 32. Tumour growth was recorded twice weekly and results are mean ± SEM (g, i, k, m) or mean % change in tumour volume ± SEM (h, j, l, n). P ≤ 0.0001 (****), P ≤ 0.001 (***), P ≤ 0.01 (**) or P ≤ 0.05 (*), as determined by two-way ANOVA and Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test