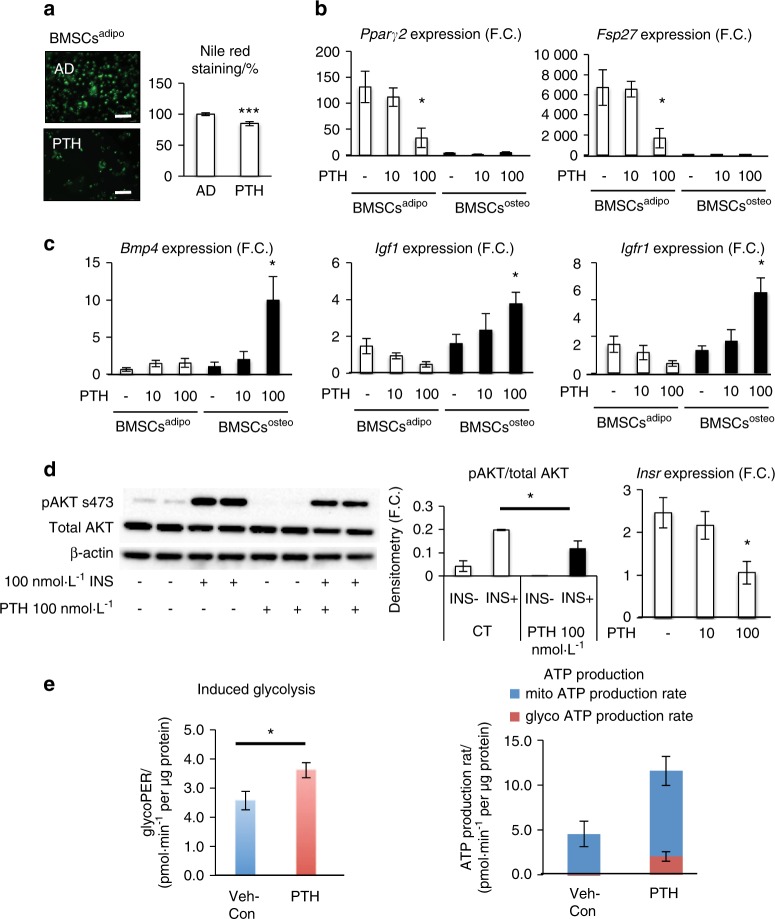
Fig. 5.
PTH affects the adipogenic potential of BMSCsadipo progenitors. Evaluation of PTH treatment on AD differentiation potential in BMSCsadipo and BMSCsosteo. a Representative pictures and evaluation of Nile Red staining in BMSCsadipo differentiated in adipogenic conditions (AD) and after chronic (D10) PTH treatment, (scale bar 100 μm); b gene expression of adipocytic and insulin signaling-related genes such as Pparγ2, Fsp27, and Irs1 after chronic PTH treatment; c gene expression of PTH-responsive genes such as Bmp4, Igf1, and Igfr1 after chronic PTH treatment; data are presented as the mean of the fold change (F.C.) over undifferentiated cells ± SEM, (n = 3) d representative western blot and densitometry of insulin-stimulated (100 nmol·L–1, 15 min) phosphorylation of AKT (p-S473AKT) and total AKT and gene expression of Insr in BMSCsadipo treated with PTH 100 nmol·L–1; (n = 3); e glycolytic potential of BMSCsadipo and ATP production after 24 h of PTH treatment (n = 3); data are presented as the mean ± SEM (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001: BMSCsadipo vs BMSCsosteo, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test)