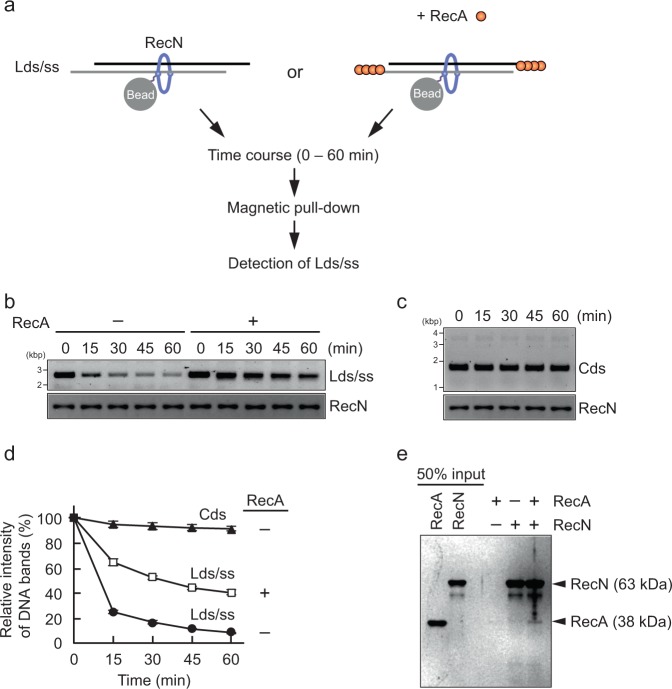
Fig. 4.
RecA prevents the release of RecN from ssDNA ends. a Schematic illustration of His pull-down assays in b. b RecN (1 µM) was mixed with a linear ds/ssDNA (Lds/ss). The RecN-Lds/ss complex was collected using Co2+-conjugated beads, washed in buffer containing 50 mM KCl. To initiate the reactions, the bead suspension was incubated in the presence or absence of RecA (1 µM) at 37 °C. Aliquots were removed for analysis at the indicated time points. The bead-bound materials were recovered and analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis (for DNA) and SDS–PAGE (for proteins). c The control experiment was performed in the absence of RecA as described for b, with the exception that pUC19 circular dsDNA (Cds) was used in place of Lds/ss. d Quantification of the band intensities of DNA substrates in the agarose gel images shown in b and c. The amount of DNA recovered at time zero was defined as 100%. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. e The physical interaction of RecN with RecA. The reaction mixtures were incubated in the presence of the indicated proteins (1 µM each protein). The proteins bound to Co2+-conjugated beads were collected, washed, eluted with SDS–sample buffer, and then analyzed by SDS–PAGE and CBB staining