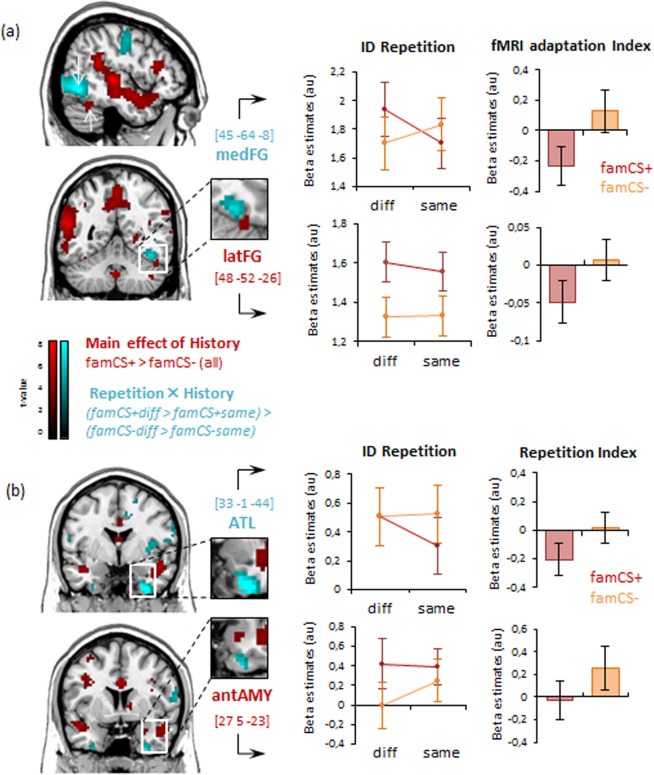
Figure 3.
Brain areas showing emotional history-related increases (in red) and repetition-related decreases (in blue) as a function of emotional learning in the priming session (see also Tables 1, 2). (a) Whole brain maps indicate a functional-anatomical segregation within the FG with the latFG showing a main effect of emotional history and the medFG showing a selective repetition suppression effect for famCS+ faces. (b) Whole brain maps show history-related increases in anterior amygdala (AMY), and a history x repetition interaction in the anterior temporal lobe (ATL). For both a) and b) plots of the activity parameters illustrates beta weights as a function of face ID repetition. An index of cross-view repetition suppression was calculated by subtracting parameters to same view condition from the different view condition. Note that plots here are shown to illustrate the results but no post-hoc statistics were performed on these data.