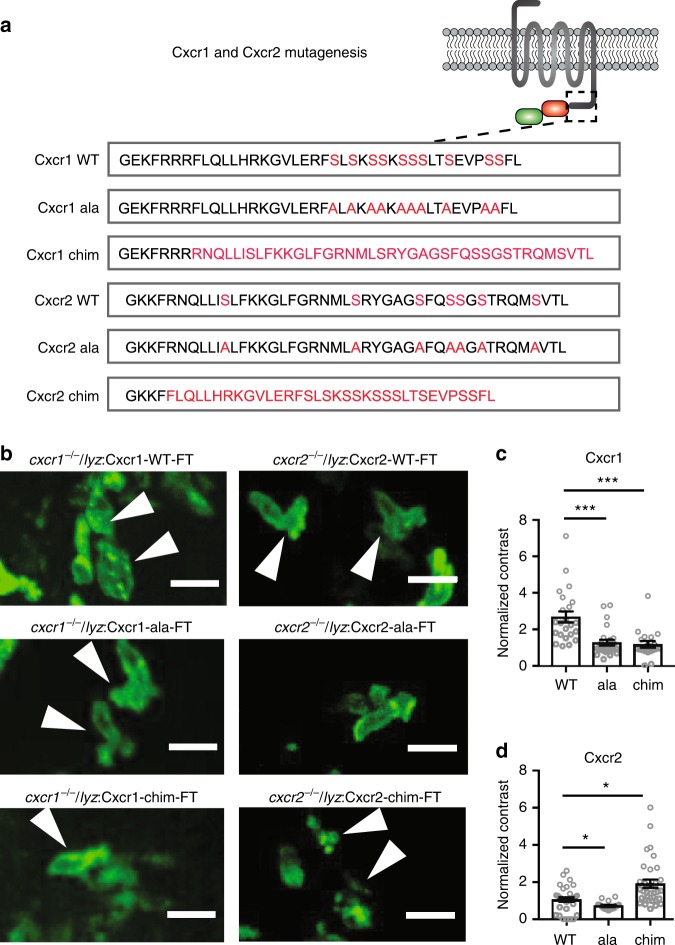
Fig. 4.
Receptor mutagenesis alters Cxcr1 and Cxcr2 trafficking. a Mutagenesis of Cxcr1. Amino acid sequence of the C-terminus is shown with candidate phosphorylation targets (serines) or transplanted sequences highlighted in red. b Neutrophils in cxcr1−/−/cxcr2−/− larvae rescued by transgenic neutrophil-specific expression of Cxcr1-FT/Cxcr2-FT, Cxcr1-ala-FT/Cxcr2-ala-FT, or Cxcr1-chim-FT/Cxcr2-chim-FT receptors. Arrows point to neutrophils at the center of the wound, with representative distribution of the receptor. Scale bar = 15 µm. c Quantification of contrast in cxcr1−/− or cxcr1−/+ neutrophils rescued by the different Cxcr1-FT receptor variants. n = 23 cells (WT) from 7 larvae, n = 26 cells (ala) from 6 larvae, n = 19 cells (chim) from 5 larvae. Data were acquired in 2 to 4 imaging sessions. Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. d Quantification of contrast in cxcr2−/− neutrophils rescued by the different Cxcr1-FT receptor variants. n = 33 cells (WT) from 5 larvae, n = 18 cells (ala) from 5 larvae, n = 33 cells (chim) from 8 larvae. Data are from independent larvae in 3 to 5 imaging sessions. Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. Error bars represent S.E.M. across cells. Source data are provided as a Source Data file