Figure 4.
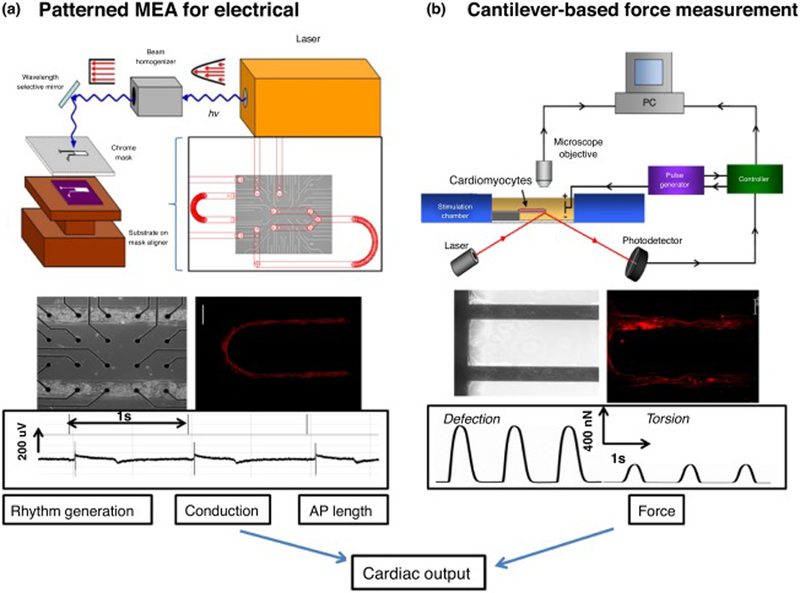
Key elements for a platform for determining cardiac physiology using human cardiomyocytes. Cardiac function was extrapolated from measurement of rhythm generation (frequency and amplitude), conduction velocity, action potential length (QT interval) and force generation of the heart (a) schematic of the system used to pattern SAMs on microelectrode arrays (MEAs) (top). Phase contrast micrograph of patterned human-derived cardiomyocytes on top of substrate-embedded extracellular electrodes. Immunostaining verified that human-derived cells differentiated to cardiomyocytes (middle) and exhibited cardiac rhythm generation as measured by the embedded electrodes (bottom). (b) Diagram of the cantilever-based force measurement system (top) cardiomyocytes integrated into the BioMEMs device and immunocytochemistry indicating cardiac alignment along the cantilever (middle). Example traces of deflection and torsional force with the device after myocyte contractions (bottom) [132].
