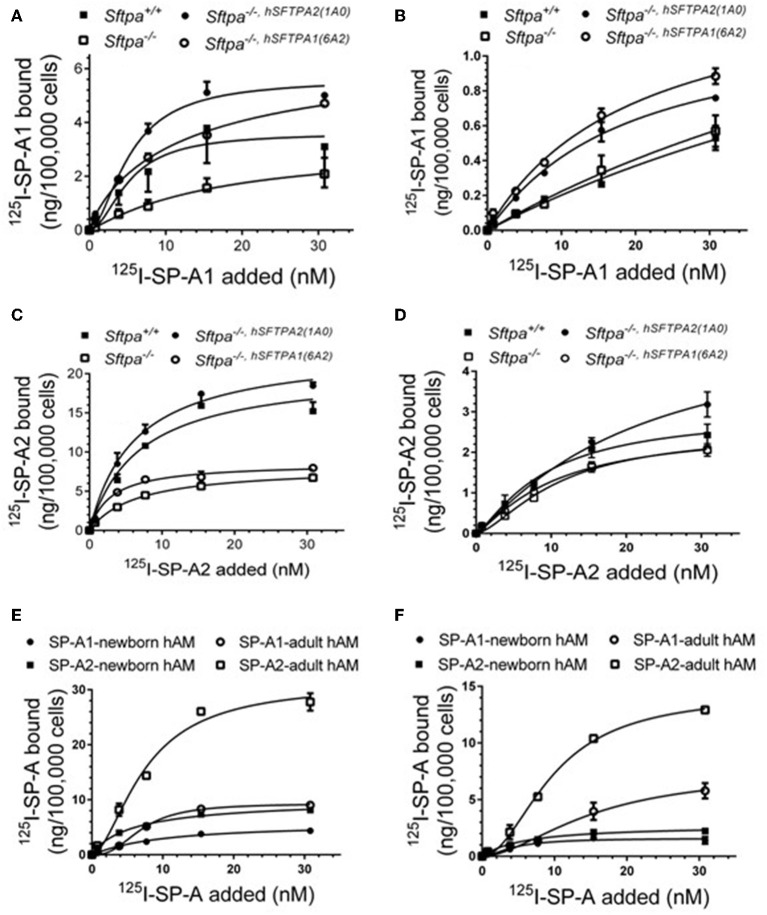
Figure 6.
Murine and human SP-A variants are paracrine regulators of SP-A binding to alveolar macrophages in postnatal lung. Binding assays were carried out with alveolar macrophages obtained from either murine lung (A–D) or human lung (E,F) using radiolabeled human SP-A1 or SP-A2 in the presence (A,C,E) or absence of calcium (B,D,F). Alveolar macrophages from murine lungs (A–D) were obtained from WT (SP-A+/+), SP-A-deficient (SP-A−/−), or humanized mice expressing either SP-A1 variant 1A0 (SP-A−/−,hSFTPA2(1A0) ), or SP-A2 variant 6A2 (SP-A−/−,hSFTPA2(6A2) ) in the absence of endogenous murine SP-A (Sftpa). Human alveolar macrophages were obtained from 6 month (E) and 20 years old (F) rejected transplant lungs. Assays were carried out at 4°C for 1.5 h at 50,0000 cells/assay. Bound SP-A was separated by centrifugation over a silicon oil mixture. Assays were performed in duplicate and data pooled from 2 independent experiments. Alveolar macrophages from mouse lungs were pooled from 10 mice per genotype to obtain sufficient number of cells per experiment. Binding isotherms were generated using Prizm software by non-linear regression analysis using the Hill equation. Data shown are Means ± SE.