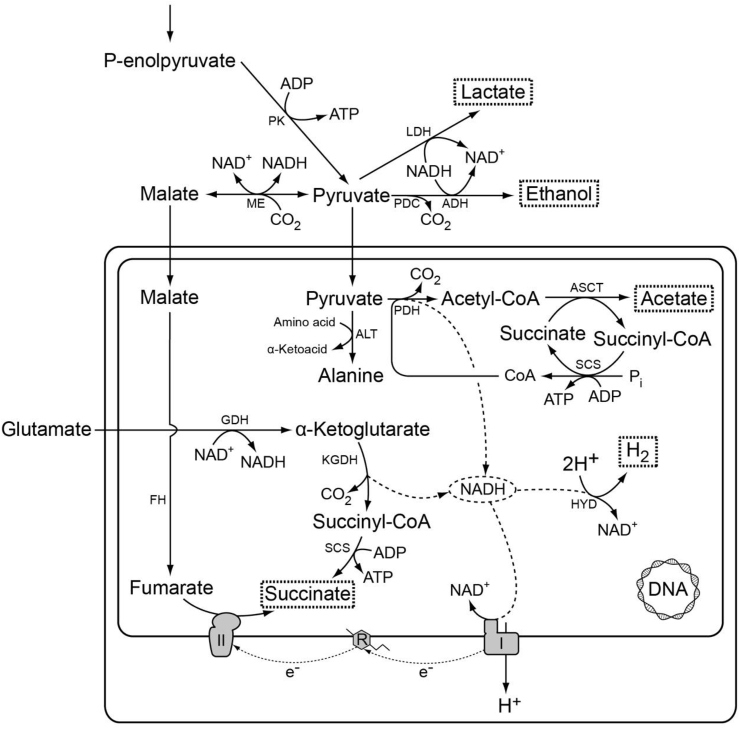
Fig. 5.
Tentative map of major pathways of energy metabolism in hydrogen-producing mitochondria of the anaerobic ciliate Nyctotherus ovalis. The map is redrawn after [47]. The incomplete Krebs cycle is likely used in the reductive direction [211]. A proton gradient is generated, probably by a functional respiratory complex I, which passes the electrons from the NADH pool through rhodoquinone to complex II, acting as fumarate reductase synthesizing succinate [208]. Redox balance is also achieved with the help of hydrogenase, releasing molecular hydrogen [113]. ATP can be synthesized by substrate-level phosphorylation, producing acetate. I, respiratory complex I; II, fumarate reductase/succinate dehydrogenase; ADH, alcohol dehydrogenase (NADH-dependent); ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ASCT, acetate:succinate CoA transferase subfamily 1A; FH fumarase; GDH, glutamate dehydrogenase; HYD, hydrogenase; KGDH, alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; ME, malic enzyme; R, rhodoquinone; PDC, pyruvate decarboxylase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; PK, pyruvate kinase; SCS, succinyl-CoA synthetase.