Figure 3.
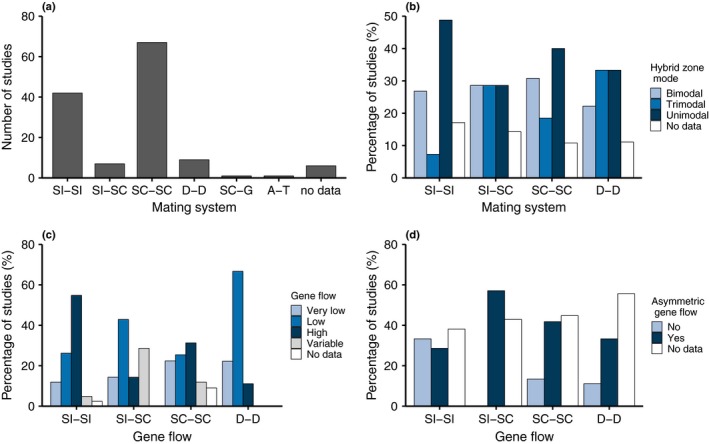
Comparative analysis for 133 angiosperm species pairs by mating system combination (see Supporting Information Table S1 for descriptions of each mating system type). (a) The number of species pairs in each mating system combination: both self‐incompatible (SI × SI, n = 42), self‐incompatible × self‐compatible (SI × SC, n = 7), both self‐compatible (SC × SC, n = 67), both dioecious (D × D, n = 9), self‐compatible × gynodioecious (SC × G, n = 1), androdioecious × trioecious (A × T, n = 1) and unknown (mating system of one or both taxa unknown, n = 6). (b) Proportion of species pairs classified as each hybrid zone mode (bimodal, trimodal and unimodal). (c) Proportion of species pairs categorized by level of gene flow (very low, low, high and variable). (d) Proportion of species pairs that recorded asymmetries in gene flow.
