Figure 2.
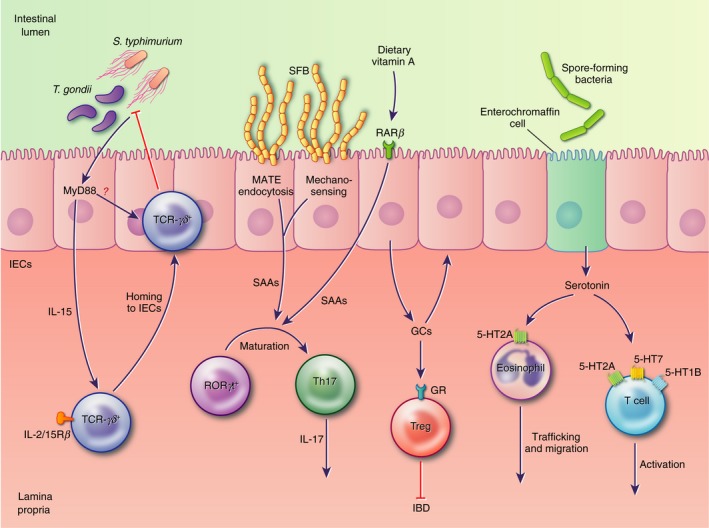
In response to microbial stimuli, intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) secrete factors that modulate various immune cell functions. In the small intestine these include interleukin‐15 (IL‐15), required for the recruitment of protective T‐cell receptor (TCR) ‐γδ + intraepiethlial lymphocytes (IELs) to the epithelial layer, and serum amyloids, which induce the differentiation of IL‐17‐secreting T helper type 17 cells. In the small and large intestine, glucocorticoids and serotonin promote anti‐inflammatory responses by immune cell populations, including lymphocytes and eosinophils, modulating inflammation and the development of disease pathology.
