Figure 4.
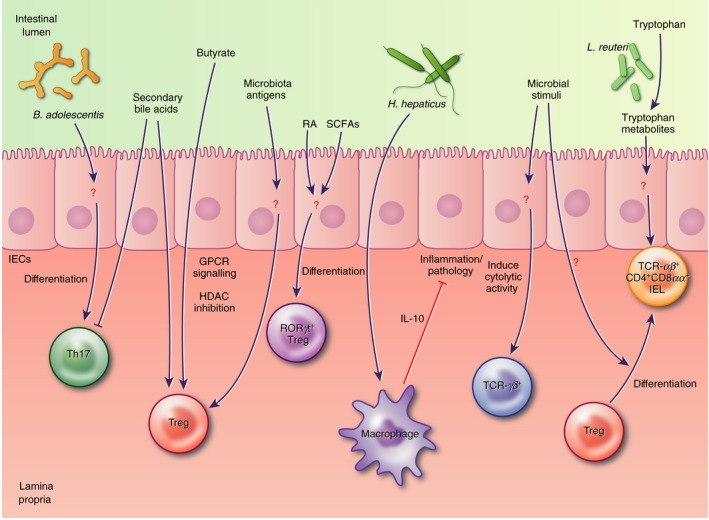
Microbial modulation of intestinal immune cells is reported to involve both direct interaction of lymphocytes and antigen‐presenting cells (APCs) with microbial stimuli, as well as relatively uncharacterized indirect interactions via intestinal epithelial cells (IECs). These interactions involve many subsets of intraepithelial and lamina propria T cells and microbial metabolites like short‐chain fatty acids, tryptophan catabolites and secondary bile acids, as well as currently undefined microbial antigens.
