Figure 5.
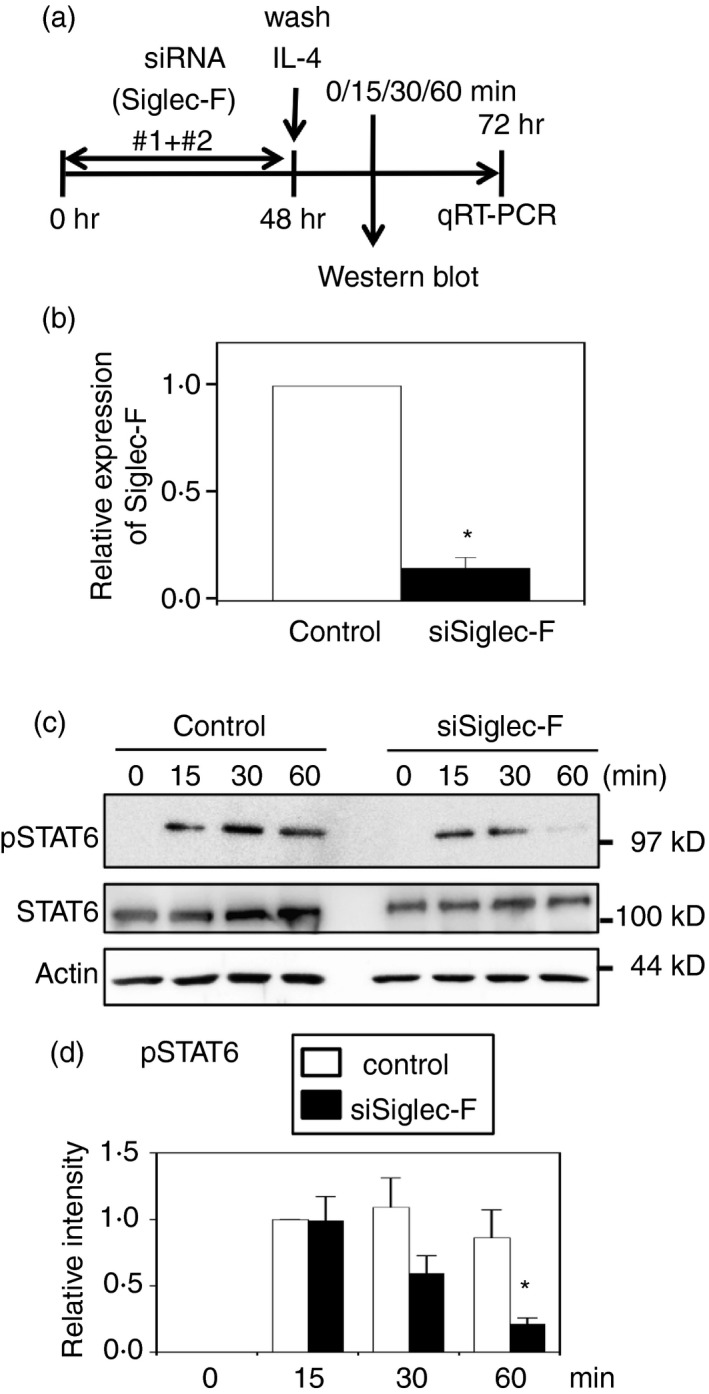
Siglec‐F knockdown reduces signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) phosphorylation induced by interleukin‐4 (IL‐4) in macrophage colony‐stimulating factor‐differentiated bone‐marrow‐derived macrophages (M‐BMDMs). (a) Schematic presentation of the knockdown experiment. M‐BMDMs were transfected with Siglec‐F or control small interfering RNA (siRNA). Cells were washed after a 48‐hr culture and stimulated with IL‐4 for the indicated periods. The phosphorylation of STAT6 was examined by Western blotting. (b) Confirmation of knockdown. Total RNA was collected 24 hr after the stimulation and subjected to qRT‐PCR. Data are the mean ± SE of six independent experiments. *P < 0·05 versus the control by Student's t‐test. (c) Siglec‐F knockdown reduced the phosphorylation of STAT6. Total and the phosphorylated form of STAT6 were examined. Actin was measured as a control. A representative result of six independent experiments is shown. (d) Quantification of band intensity. The band intensity of pSTAT6 was normalized to that of actin. The band intensity of control siRNA at 15 min was regarded as 1. White and black bars indicate control and Siglec‐F siRNAs, respectively. Data are the mean ± SE of six independent experiments. *P < 0·05 versus the control at the same time point by Student's t‐test.
