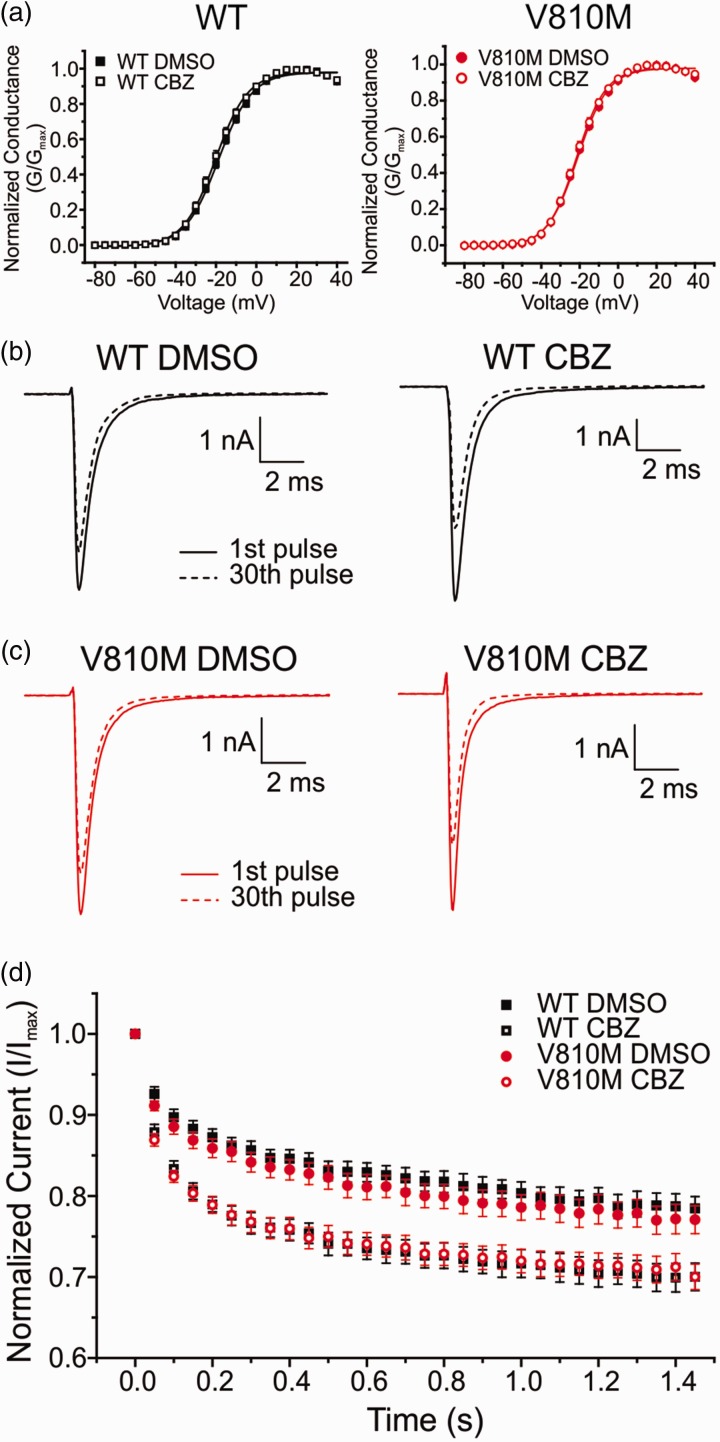
Figure 5.
CBZ enhances use-dependent inhibition of V810M and WT channels. (a) Voltage-dependent activation of WT (left; DMSO: solid black squares, n = 15; CBZ: open black squares, n = 12) and V810M (right; DMSO: solid red circles, n = 15; CBZ: open red circles, n = 13) channels show no shift in activation following a 30-min preincubation period with 30 µM CBZ as compared to 0.1% DMSO vehicle. Conductance curves were normalized to the maximum conductance value and fit to a Boltzmann equation. (b) Representative traces of use-dependent inhibition of WT channels following a 30-min preincubation period with either 0.1% DMSO vehicle (left) or 30 µM CBZ (right). (c) Representative traces of use-dependent inhibition of V810M channels following a 30-min preincubation period with either 0.1% DMSO vehicle (left) or 30 µM CBZ (right). (d) Use-dependent inhibition curves of WT (DMSO: solid black squares, n = 15; CBZ: open black squares, n = 12) and V810M (DMSO: solid red circles, n = 14; CBZ: open red circles, n = 12) channels showing a significant difference between DMSO and CBZ conditions for both channels (p < 0.05). Use-dependent inhibition was recorded at 20 Hz and defined as the ratio of peak current of the 30th pulse normalized to peak current of the first pulse. CBZ: carbamazepine; DMSO: dimethyl sulfoxide.