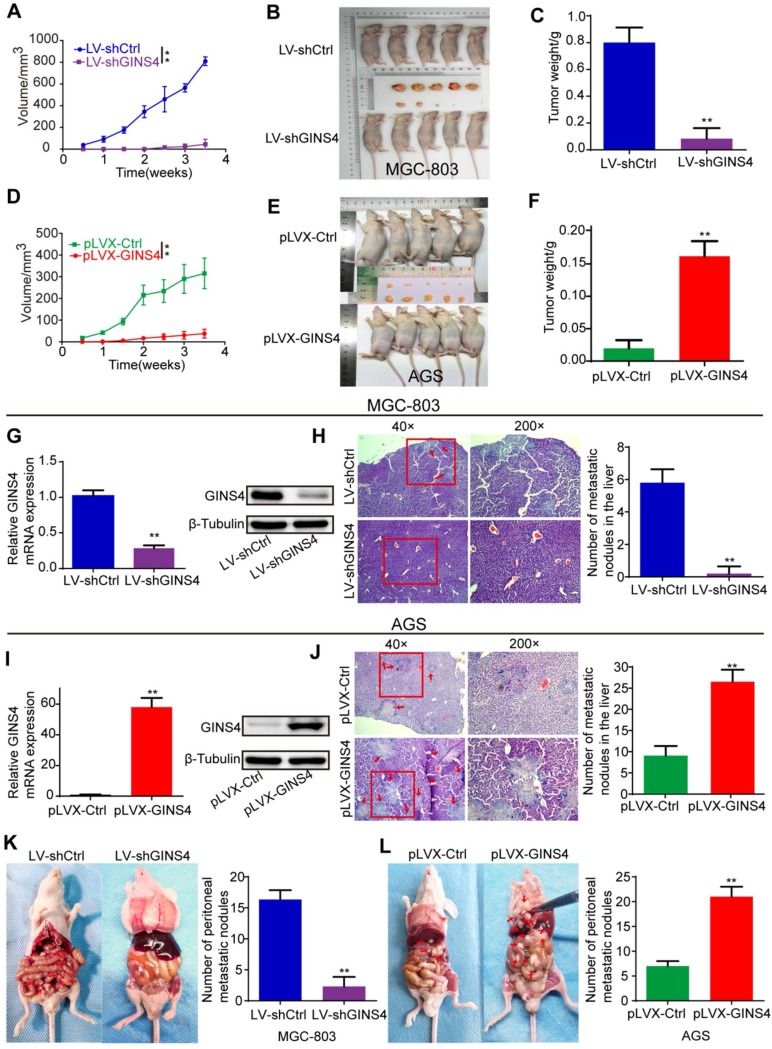
Figure 4.
GINS4 promotes cell growth and metastasis of gastric cancer in vivo. A-F, a nude mouse xenograft model was constructed. A, Tumor volumes of MGC-803 cells were measured 2 times every week for 4 weeks. B, Images of subcutaneous xenograft tumors of MGC-803 cells. C, The final tumor weight of MGC-803 cells was shown. D, Tumor volumes of AGS cells were measured 2 times every week for 4 weeks. E, Images of subcutaneous xenograft tumors of AGS cells. F, The final tumor weight of AGS cells was shown. G, The expression of GINS4 mRNA and protein in tumors with MGC-803/LV-shGINS4 was significantly lower than that in tumors with MGC-803/LV-shCtrl. H, Representative images of HE staining of the liver metastasis. Knockdown of GINS4 decreased the number of the liver metastatic nodules compared with negative control. I, The expression of GINS4 mRNA and protein in tumors with AGS/pLVX-GINS4 was significantly higher compared with that in tumors with AGS/pLVX-Ctrl. J, Representative images of HE staining of the liver metastasis. Overexpression of GINS4 increased the number of the liver metastatic nodules compared with negative control. K&L, Representative images of peritoneal metastasis assays. Knockdown of GINS4 decreased the number of peritoneal metastatic nodules (K), whereas overexpression of GINS4 increased the number of peritoneal metastatic nodules (L) **P < 0.01.