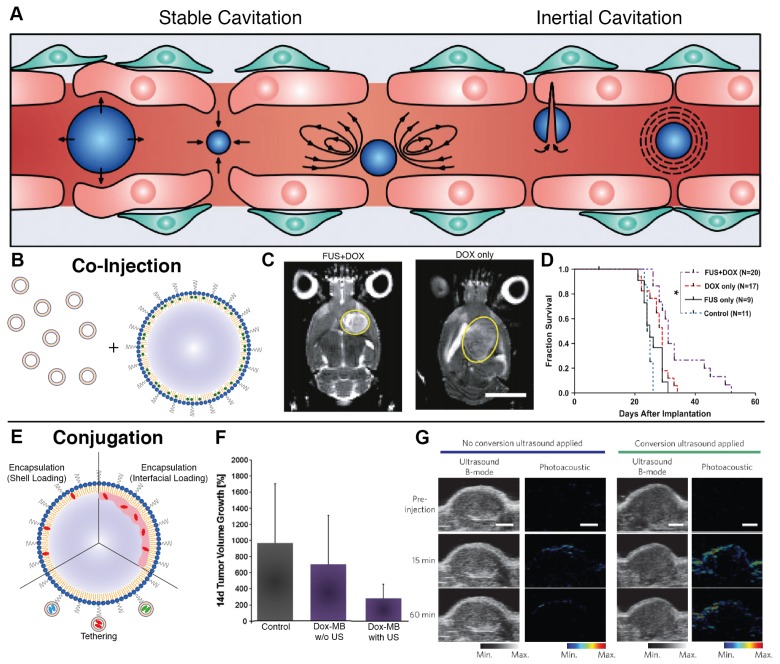
Figure 2.
A. Cavitation-based mechanisms by which ultrasound can enhance nanomedicine delivery, including transient disruption through stable cavitation and destructive opening through inertial cavitation (adapted from 157). B. Co-injection involves simultaneous administration of microbubbles and nanoparticles with ultrasound priming to improve delivery. C-D. Application of microbubble-enhanced focused ultrasound and pre-administered liposomal doxorubicin on rat brains bearing 9L glioma xenografts results in tumor size reduction and prolonged survival compared to doxorubicin only controls (adapted from 75). E. Conjugation encompasses both nanoparticle tethering and agent encapsulation to produce a highly co-localized platform for delivery improvement. F. The combination of doxorubicin-loaded microbubbles and ultrasound achieve enhanced therapeutic reduction in DSL6A pancreatic xenograft size compared to drug-loaded bubbles alone (adapted from 90). G. In situ microbubble-to-nanoparticle conversion of porphyrin-lipid microbubbles upon ultrasound irradiation leads to enhanced nanoparticle delivery as measured by photoacoustic imaging (adapted from 156).