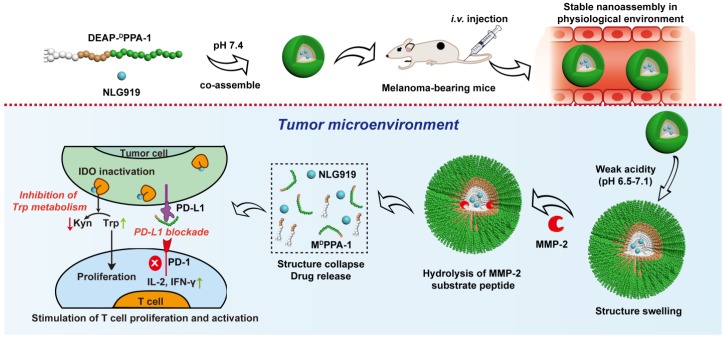
Figure 2.
Composition and the proposed antitumor mechanism of the NLG919@DEAP-DPPA-1 nanoparticle. DEAP-DPPA-1 and NLG919 were co-assembled into a nanoparticle and maintained stable nanostructure at the physiological environment. In acidic tumor conditions, the hydrophobic core of the nanoparticle allowed MMP-2 to hydrolyze its substrate peptide leading to the complete dissociation of the nanostructure. Thereafter, NLG919 and MDPPA-1 were released for blocking the immunosuppressive pathways, IDO and PD-L1, respectively. Adapted with permission from 72, copyright 2018 American Chemical Society.