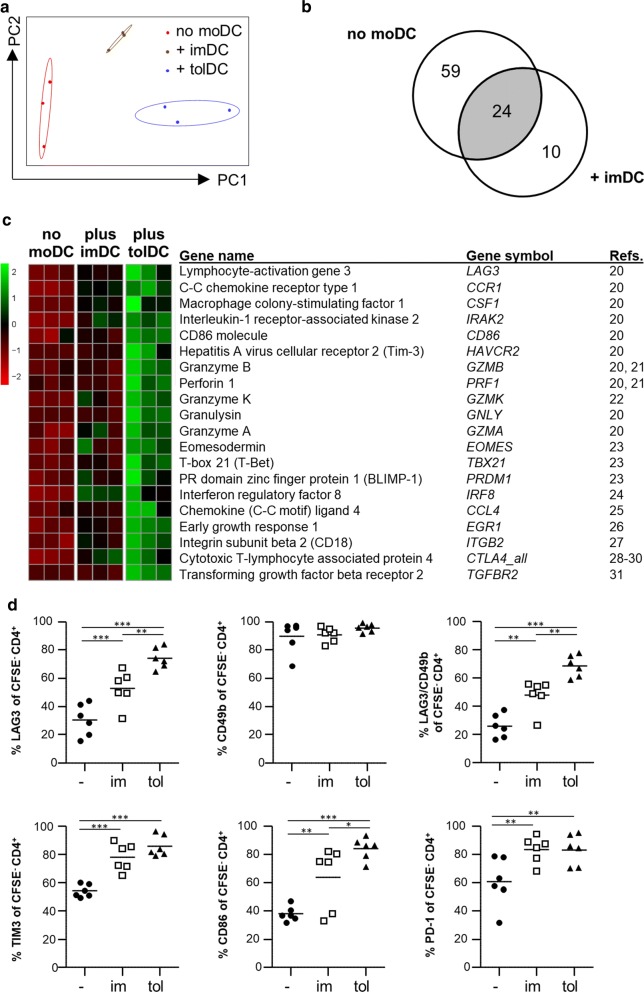
Fig. 2.
tolDC induce a Tr1 phenotype in antigen-specific CD4+ T cells. Cell proliferation dye (CFSE/CTV)-labelled PBMC of healthy controls were cultured with the recall antigen PPD and tolDC (tol), imDC (im) or without addition of any type of moDC (−) for 9 days. a–d 100,000 CFSE/CTV− life CD4+ T-cells were sorted by FACS. Cell were then lysed and gene expression determined by the NanoString nCounter platform. a Principal component analysis (PCA) plot showing clustering of the different groups. PC1: principal component 1; PC2 principal component 2. b Venn diagram showing genes differentially expressed (BH P ≤ 0.1) with at least a 1.5-fold change for control (no moDC) PPD T-cells (left circle) and imDC-PPD T-cells (right circle) compared to tolDC-PPD T-cells. The numbers in the circles indicate the modulated genes for each condition. The grey area represents the overlap between both conditions. d Heat map of Tr1-related gene expression levels that were significantly (BH P ≤ 0.1) differentially expressed with at least a 1.5-fold change in tolDC-PPD T-cells compared to control (no moDC) PPD T-cells. e Percentages of LAG3, CD49b, TIM3, CD86 and PD-1 in CFSE/CTV− live CD4+ T-cells were measured using flow cytometry. Repeated measures analysis of variance was used. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001