Figure 4 (A-D).
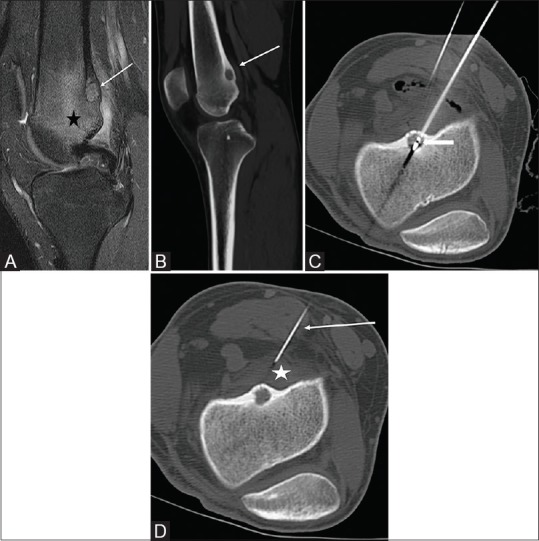
(A) Fat suppressed sagittal MRI of the knee with edema in the distal femur (black star). There is a hyperintense lesion in the posterior cortex of the distal femur (white arrow) suggestive of an OO nidus. (B) The margins of the nidus are better seen on the CT (white arrow). (C) Ablation probe in the nidus (white arrow). (D) A 20 G needle (white arrow) is placed in the popliteal fossa adjacent to the nidus and used to infuse D5W (white star) to protect the adjacent nerves from thermal damage
