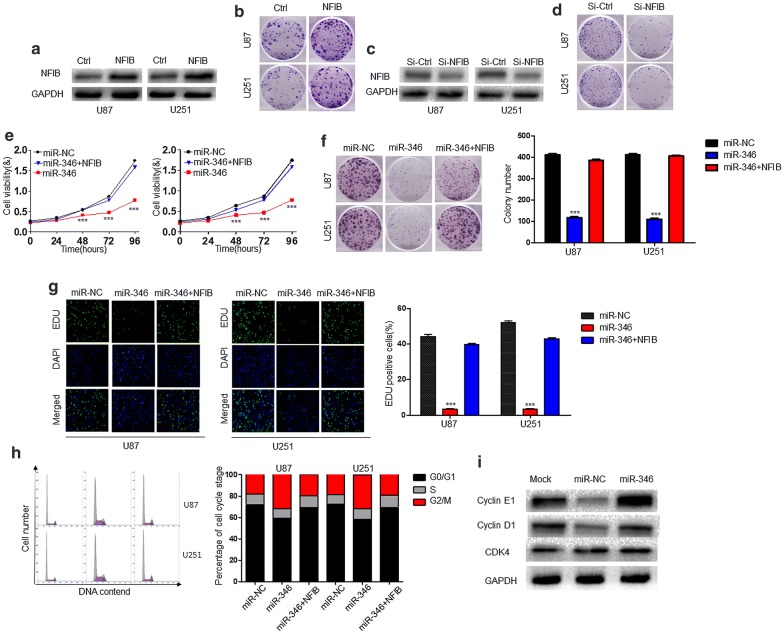
Fig. 4.
NFIB overexpression reverses the suppressive effects of miR-346 on glioma cells in vitro. a Western blot analysis of NFIB expression in U87 and U251 cells expressing control (Ctrl) or NFIB overexpression vectors. GAPDH served as the loading control. b Representative images and quantification of colony-forming assays of control or NFIB-overexpressing U87 and U251 cells. c Western blot analysis of NFIB expression in U87 and U251 cells after transfection with control (si-Ctrl) or NFIB-targeting siRNA (si-NFIB). GAPDH served as the loading control. d Representative images and quantification of colony-forming assays of U87 and U251 cells transfected with si-NFIB or si-Ctrl. e–h CCK-8 viability assay (e), colony-forming assay (f), EDU proliferation assay (g), and cell cycle distribution assay (h) of U87 and U251 cells transfected with miR-NC, miR-346, or miR-346 + NFIB. i Western blot analysis of NFIB and downstream effector proteins Cyclin E1, Cyclin D1 and CDK4 in U87 and U251 cells transfected with miR-NC, miR-346, or miR-346 + NFIB. GAPDH was used as the loading control. ***P < 0.001