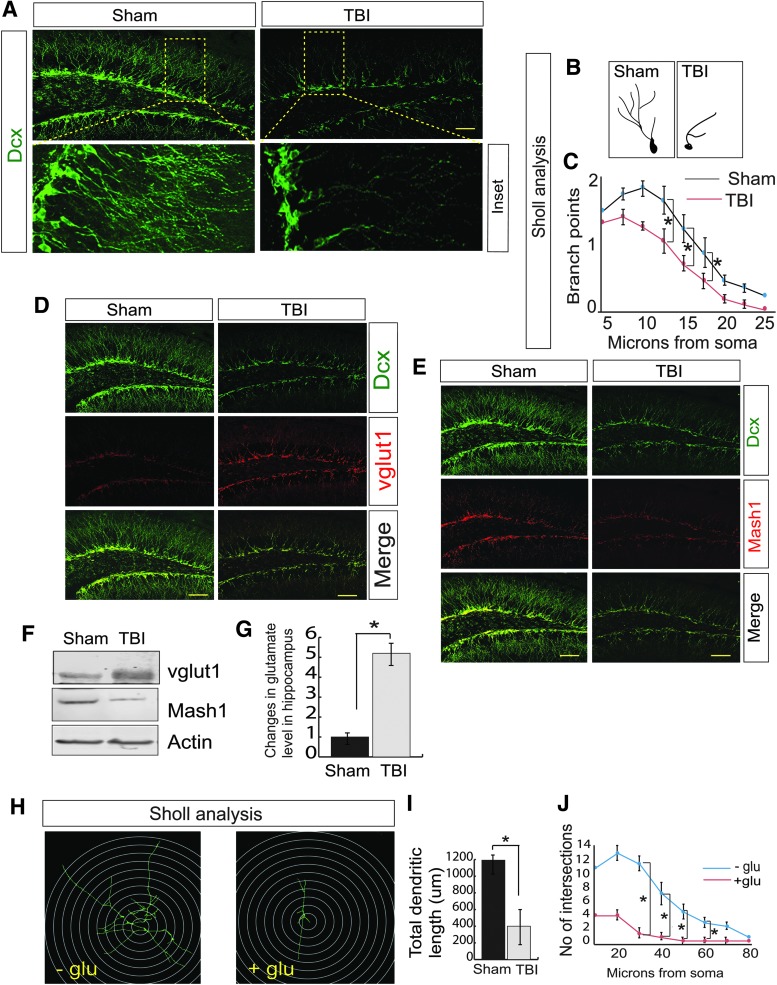
FIG 1.
TBI leads to a decrease in neurogenesis in association with an increase in vGlut1-positive cells but a decrease in Mash1-positive cells. (A) Confocal microscopic studies showed that Dcx-positive cells were decreased significantly in the DG of the hippocampus following TBI. (B,C) The Sholl analysis of the branch points of Dcx-positive cells was decreased in DG of TBI mice compared with sham mice. (D) Confocal microscopic studies showed that vGlut1-positive cells were increased significantly in the DG of the hippocampus following TBI. (E) Confocal microscopic studies showed that Mash1-positive cells were decreased significantly in the DG of the hippocampus following TBI. (F) Western blot analysis to monitor the expression level of vGlut1 and Mash1 in both sham and TBI mice. (G) The glutamate level was increased in the hippocampus of TBI mice. (H–J) Neuronal stem cells isolated from mice were treated with glutamate and Sholl analysis (H) shows that glutamate treatment affects total dendritic length (I) and a number of intersections (J). Statistical significance was measured by one-way ANOVA with a Tukey-Kramer post hoc correction, n = 7, *p < 0.05. All data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Scale bar = 20 μm. ANOVA, analysis of variance; DG, dentate gyrus; Dcx, Doublecortin; SEM, standard error of the mean; TBI, traumatic brain injury; vGlut1, vesicular glutamate transporter 1. Color image is available online.