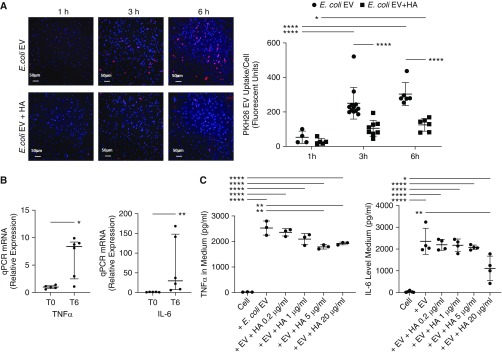
Figure 5.
Update of Escherichia coli extracellular vesicles (EVs) by human monocytes. (A) The normal uptake of PKH26-labeled E. coli EVs by human monocytes was inhibited by coincubation with high-molecular-weight (HMW) hyaluronic acid (HA) by fluorescent microscopy as quantified by the average fluorescence intensity of PKH26 for each cell (scale bars, 50 μm). (B) Compared with EVs released from healthy lungs, E. coli EVs contained significantly higher mRNA levels of the inflammatory cytokines TNFα (tumor necrosis factor α) and IL-6 at 6 hours. (C) Coincubation of human monocytes with HMW HA decreased the release of TNFα and IL-6 caused by E. coli EVs by 29% and 53%, respectively, by human monocytes. Data are mean ± SD for PKH26 E. coli EV uptake and TNFα and IL-6 levels. Data are median with interquartile range for PCR data. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ****P < 0.0001 by ANOVA (Bonferroni) in C, ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test in A, and Mann-Whitney test in B; n = 3–12. P values and confidence intervals are shown in Table E1. qPCR = quantitative PCR.