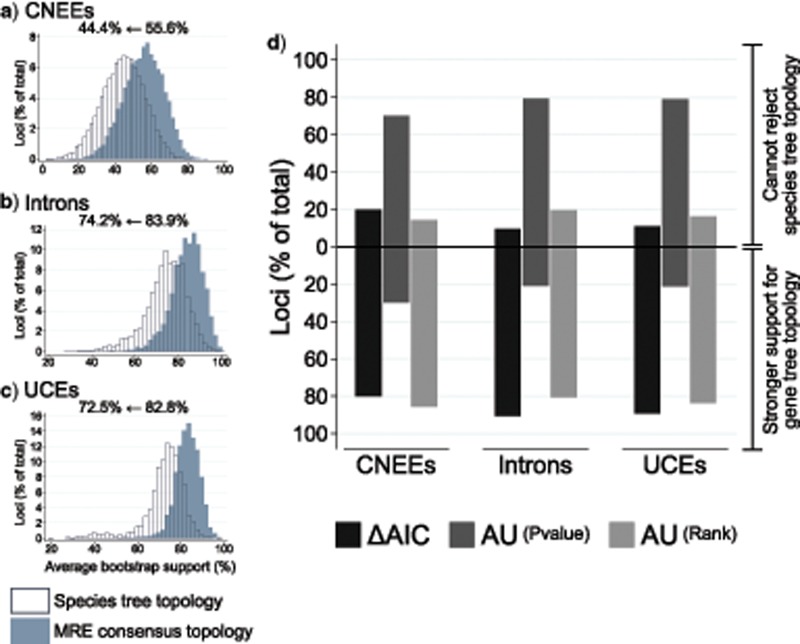
Figure 7.
Support for observed topological heterogeneity in estimated gene trees. (a–c) Distributions for the average bootstrap support for all clades recovered in majority rule extended consensus gene trees (“MRE consensus topology”, drawn as solid bars), and the average support when bootstrap replicates for each gene are constrained to the inferred species tree topology (open bars) are shown for CNEEs (a), introns (b), and UCEs (c). Values above each panel indicate the decrease in the grand mean of average support across genes when bootstrap replicates are constrained to the species tree topology. (d) Support that observed gene tree topologies differs from the inferred species tree. Dark gray bars indicate the difference in AIC from values calculated using the MRE consensus topology for each gene, relative to that obtained when the sequence alignment is constrained to the species tree topology. The baseline at 0 corresponds to 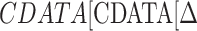 AIC = -2, thus values beneath this line indicate loci where likelihood values support the gene tree topology substantially better than that of the species tree. Results of AU tests are indicated with medium gray bars showing the proportion of loci that reject (below baseline) and fail to reject (above baseline) the species tree topology at a
AIC = -2, thus values beneath this line indicate loci where likelihood values support the gene tree topology substantially better than that of the species tree. Results of AU tests are indicated with medium gray bars showing the proportion of loci that reject (below baseline) and fail to reject (above baseline) the species tree topology at a 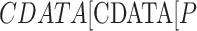 -value cutoff of 0.05, and light gray bars showing the proportion of loci where the species tree topology occurs among the top 5% of candidate topologies (above baseline), or is within the bottom 95% of tested topologies (below baseline) for AU
-value cutoff of 0.05, and light gray bars showing the proportion of loci where the species tree topology occurs among the top 5% of candidate topologies (above baseline), or is within the bottom 95% of tested topologies (below baseline) for AU 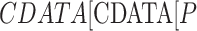 -values ranked in ascending order. AU tests for the 105 and 1575 candidate tree sets produced similar results and are shown for the 105 candidate set only.
-values ranked in ascending order. AU tests for the 105 and 1575 candidate tree sets produced similar results and are shown for the 105 candidate set only.