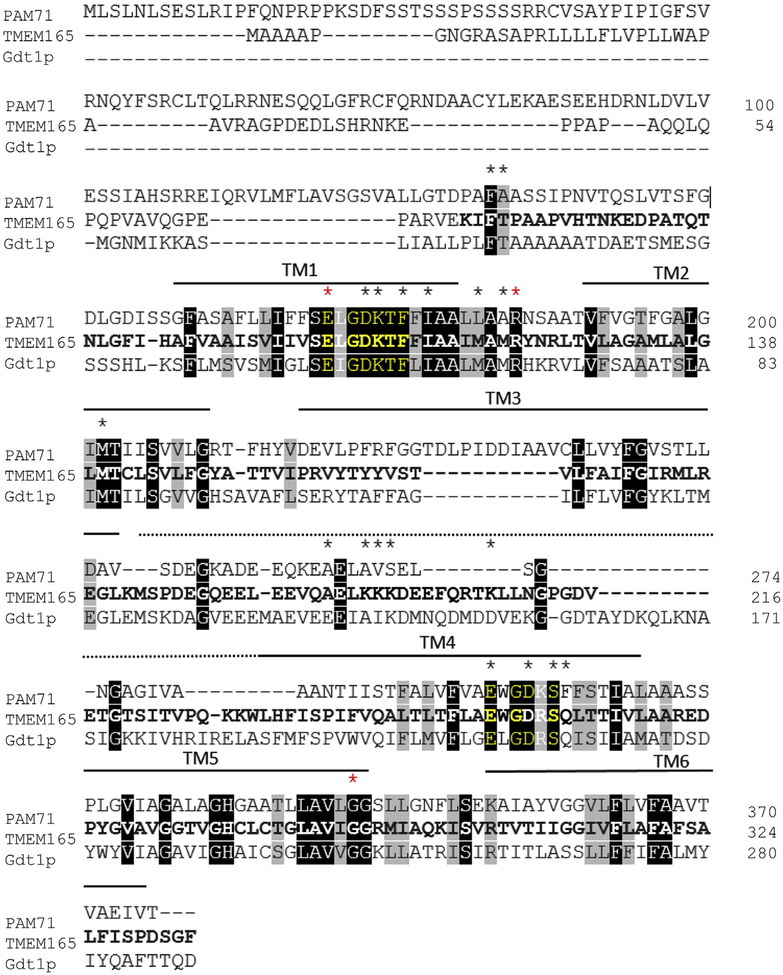
Fig. 1. Protein sequence alignment of TMEM165 and its orthologs PAM71 from Arabidopsis thaliana and Gdt1p from Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
The sequences were found in Uniprot database (www.uniprot.org) and the protein sequence alignment was generated using Clustal Omega (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo). Black boxes indicate the amino acid residues that are identical whereas gray boxes show the homologous amino acid residues. The black asterisks indicate the position of the generated mutated amino acids. The red asterisks indicate the mutated amino acids found in TMEM165-CDG patients’ proteins. The bold characters correspond to the amino acid residues that are found conserved in the mammalian TMEM165 sequence (SwissProt Database) using the Cobalt-NCBI multiple alignment tool (NCBI). Conserved domains (motif 1 and 2) are highlighted in yellow. Black horizontal bars on the top of the sequences indicate the amino acids within the predictive transmembrane domains (TMHMM v2.0 server tool). The dotted line indicates the cytosolic central loop.