Figure 5. PKM2 regulates Hh/Gli activity.
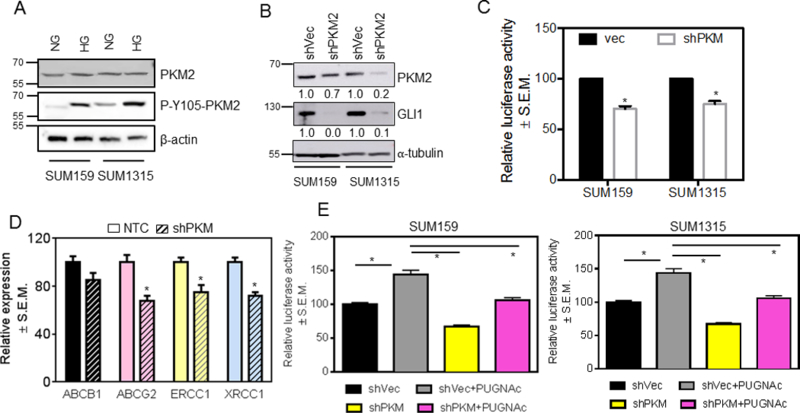
A, under high glucose conditions, the inactive form of PKM2, P-Y105, is increased. B, knocking-down PKM2 causes a decrease in protein levels of GLI1. The numbers beneath each panel represent relative signal intensity (shVec versus shPKM2) normalized to respective loading control. C, knocking-down PKM2 also inhibits the activity of GLI as shown by a decrease in activity of the 8X-GLI luciferase reporter (p=0.002 for SUM159; p=0.004 for SUM1315). D, knocking down PKM2 in SUM159 cells decreases expression of multi-drug-resistance (ABCB1 and ABCG2 (p=0.007)) and DNA-damage-repair (ERCC1 (p=0.04) and XRCC1 (p=0.005)) genes relative to control cells (transfected with non-targeting control siRNA, NTC). E, the effect on GLI1 activity of knocking-down PKM2 is reversed by the inhibition of OGA with PUGNAc (p<0.005 for all comparisons). The unpaired t-test was used for analysis.
