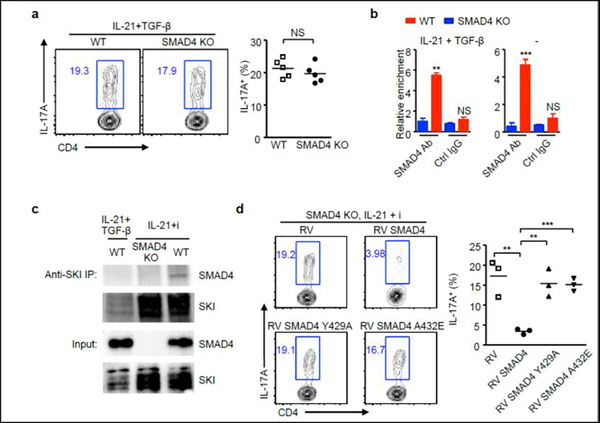
Figure 4. TGF-β disrupts SKI-SMAD4 interaction to facilitate IL-21-induced Th17 differentiation.
(a) CD4+ T cells isolated from wild-type (WT) and Cd4-cre;Smad4fl/fl (SMAD4 KO) mice were cultured with IL-21 and TGF-β. After 4 days, IL-17A+ cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. Representative results and statistical analysis are shown. (b) CD4+ T cells isolated from wild-type (WT) and Cd4-cre;Smad4fl/fl (SMAD4 KO) mice were cultured in the presence of absence of IL-21 plus TGF-β, cells were harvested after 3 days. ChIP assay was performed with control IgG antibody or SMAD4 antibody. The relative enrichment of SMAD4 binding to the Rorc locus was determined. (c) CD4+ T cells isolated from wild-type (WT) and Cd4-cre;Smad4fl/fl (SMAD4 KO) mice were cultured under indicated conditions, cells were harvested after 3 days.
Immunoprecipitation was performed with SKI antibody. Protein expression of SMAD4 and SKI was detected by immunoblotting. (d) CD4+ T cells isolated from Cd4-cre;Smad4fl/fl (SMAD4 KO) mice were cultured with IL-21 and TGF-β receptor I inhibitor (i), and then transduced with control retrovirus (RV), or retroviruses expressing wild-type form (RV SMAD4) or mutant form SMAD4 (RV SMAD4 Y429A or RV SMAD4 A432E). IL-17A+ cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. Representative results and statistical analysis are shown.