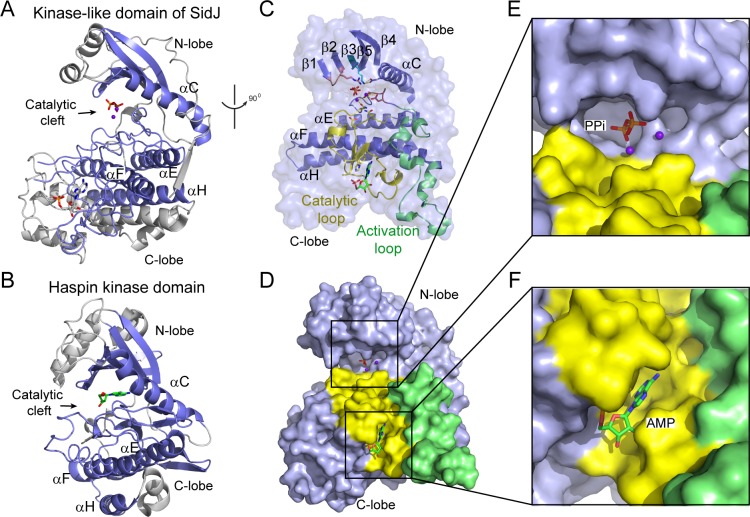
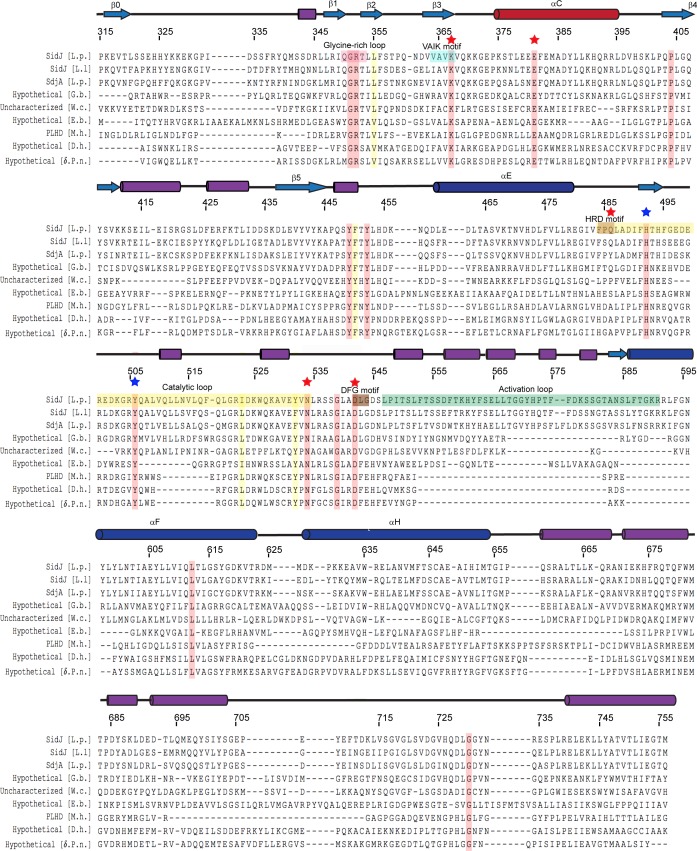
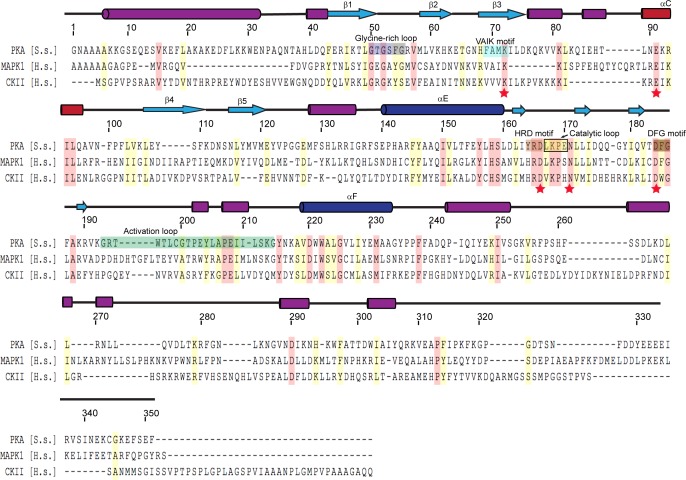
Figure 3. The core of SidJ adopts a protein kinase fold.
(A) Cartoon diagram of the kinase-like domain of SidJ. Secondary structure elements that are conserved in protein kinases are colored in blue. Ca2+ ions are shown as purple spheres while the pyrophosphate and AMP molecules are shown in sticks. (B) Cartoon representation of the kinase domain of Haspin kinase (PDB ID: 2WB6). The conserved structural core, colored in blue, is displayed with an orientation similar to that in panel (A). (C) An orthogonal view of the conserved secondary structural elements in the SidJ kinase-like domain. The N-lobe is comprised of five antiparallel β-strands and an αC helix. The C-lobe is primarily α helical. Secondary structural features are named according to PKA nomenclature. The activation loop is colored in green, the catalytic loop in yellow, and the glycine-rich loop in pink. Conserved residues within the kinase-like catalytic cleft are represented by sticks. (D) Surface representation of the SidJ kinase-like domain, depicting the catalytic cleft formed between the N- and C-lobes and the migrated nucleotide-binding site formed mainly by residues within the catalytic loop (yellow). The activation loop (green) makes close contact with the catalytic loop. (E) Enlarged view of the catalytic clefts outlined in (D). The kinase catalytic cleft contains two Ca2+ ions and a pyrophosphate (PPi) molecule. (F) Expanded view of the migrated nucleotide-binding pocket bound with an AMP.