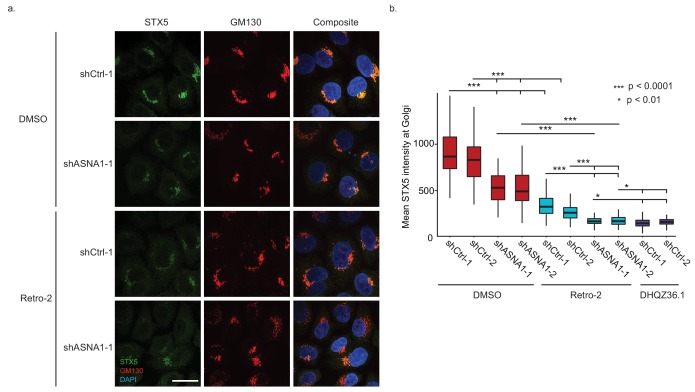
Figure 3. ASNA1 knockdown and Retro-2 treatment both decrease the abundance of Golgi-localized STX5, an ASNA1 substrate.
(A) HeLa cells expressing either ASNA1-targeting or scrambled control (shCtrl) shRNAs were treated for 24 hr with DMSO or 10 μM Retro-2 before fixation and staining for STX5, a Golgi marker (GM130), and a nuclear marker (DAPI). Shown are maximal signal projections of z-stacked confocal micrographs taken with a 100× objective and made without contrast or LUT adjustments. Scale bar represents 25 µm and applies to all images. (B) HeLa cells were treated as in part a) but including additional shRNAs and the hyperactive Retro-2 analog DHQZ36.1. Images were collected using a 60× objective and quantitatively analyzed. Shown are box plots of per cell mean STX5 intensity at GM130-marked Golgi for the indicated treatments. Asterisks specify significant differences between treatments as calculated by the MW U test.