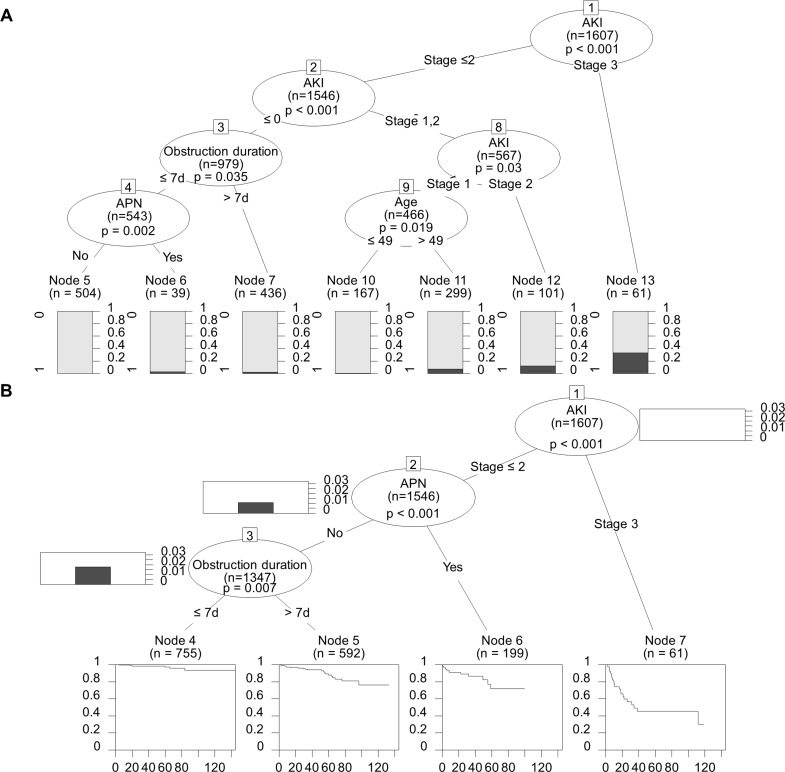
Figure 4.
Tree analyses. (A) In a decision tree model, AKI was the most important risk factor for the GFR decrease >50% (p<0.001). The second most important risk factor was AKI stage II (p=0.03). An age >49 years at the time of obstructive uropathy was selected at the next node in the group of patients with AKI stage I (p=0.019). Concomitant APN during the obstruction episode was presented for the next node in the group of patients without AKI and the obstruction duration is <7 days (p=0.002). An obstruction duration >7 days was selected at the next node, in the group of patients without AKI (p=0.035). (B) In a survival tree analysis with the variables sex, age, APN, AKI stage and obstruction duration groups, AKI stage III (p<0.001) was the most potent factor for the development of a GFR decrease >50%; APN was the second highest factor (p<0.001). An obstruction duration of more than 7 days (p=0.007) was also an independent risk factor for major renal outcomes in the survival tree analysis. AKI, acute kidney injury; APN, acute pyelonephritis; GFR, glomerular filtration rate.