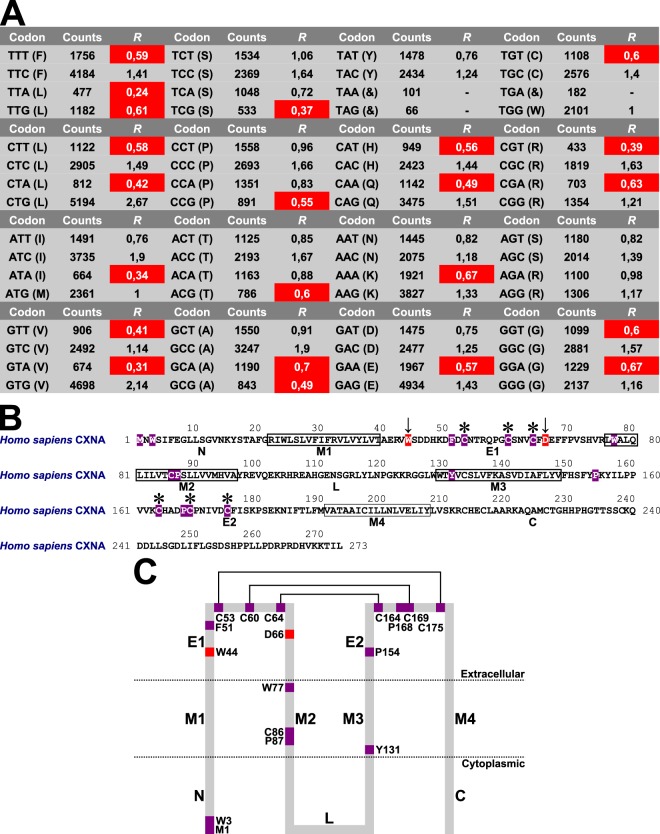
Figure 3.
Tests of protein molecular evolution of eutherian connexins. (A) Relative synonymous codon usage statistics of eutherian CXN gene data set. The not preferable amino acid codons were indicated by white letters on red backgrounds. Counts, observed amino acid codon counts; R, relative synonymous codon usage statistics; &, stop codons. (B) Reference human CXNA protein amino acid sequence. Using white letters on violet backgrounds, the 15 invariant amino acid sites were shown. The 2 forward amino acid sites were indicated by arrows and shown using white letters on red backgrounds. The connexin amino acid signature common cysteine amino acid residues that were implicated in disulfide bonding were labelled by stars. The N-terminal and C-terminal boundaries of transmembrane α-helices 1–4 were described according to Nicholson10 and Sosinsky and Nicholson11. (C) Distribution of invariant and forward amino acid sites in human CXNA protein regions. The 15 invariant amino acid sites were shown using violet squares, and 2 forward amino acid sites were shown using red squares. The common cysteine amino acid residues that were implicated in disulfide bonding were connected by lines. C, C-terminal domain; E1 and E2, extracellular connexin regions 1 and 2; L, cytoplasmic loop; M1–M4, transmembrane α-helices 1–4; N, N-terminus.