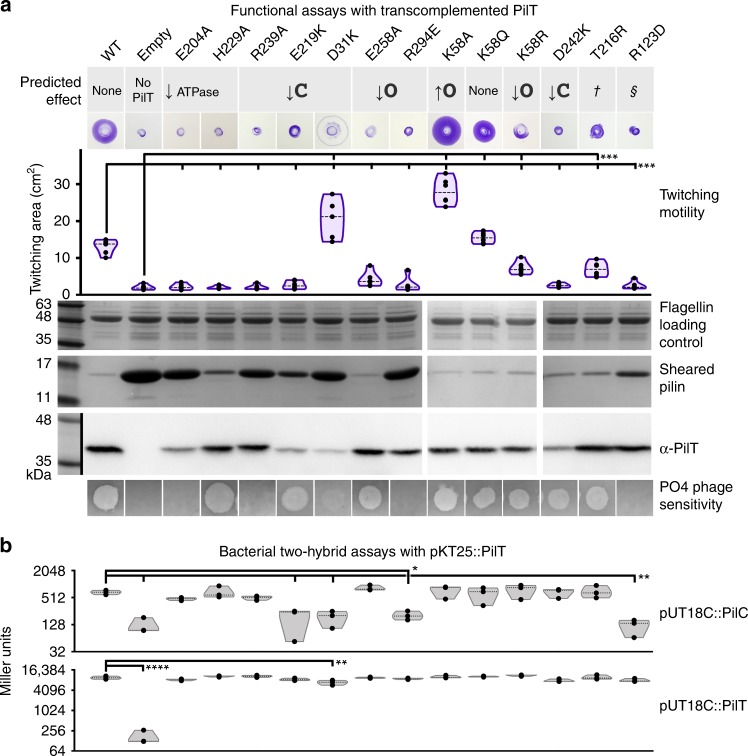
Fig. 5.
Multiple conformations and both open- and closed interfaces are essential for PilT in vivo function. a A P. aeruginosa PAO1 PilT deletion mutant was transcomplemented with wild type (WT), a vector control (Empty), and various site mutants. Their predicted effects are indicated. Dagger symbol, the T216R mutant is predicted to ablate the OOOOOO conformation. Section sign symbol, the R123D mutant is predicted to reduce the stability of the OOOOOO or CCCCCC conformations. Twitching motility was assayed by crystal violet staining (purple zones), and the areas covered by the bacteria were measured (purple violin plot, n = 6). Mean twitching areas were compared with the one-way ANOVA test, noted with black lines; reported p-values were less than 0.001 (***). Transcomplemented bacteria were grown on a surface; pilins and flagellins were sheared from the surface of the bacteria and assayed by SDS-PAGE analysis, while whole- cell lysates were probed with an anti-PilT antibody (middle). PO4 phage was spotted onto double-layer agar inoculated with the transcomplemented bacteria; transilluminated images of the resulting zones of lysis are shown (bottom). b Quantitative bacterial two-hybrid analysis of PilTPa mutants. The mutations in a were introduced into the pKT25::PilTPa two-hybrid construct. The adenylate cyclase mutant, E. coli BTH101 was then co-transformed with that construct and either pUT18C::PilCPa (top gray violin plot, n = 3) or pKT25::PilTPa (bottom gray violin plot, n = 3) and interactions assessed by measuring β-galactosidase activity in Miller units. The mean Miller units were compared with the one-way ANOVA test, noted with black lines; reported p-values were less than 0.02 (*), 0.01 (**), or 0.0001 (****). Source data are provided as a Source Data file