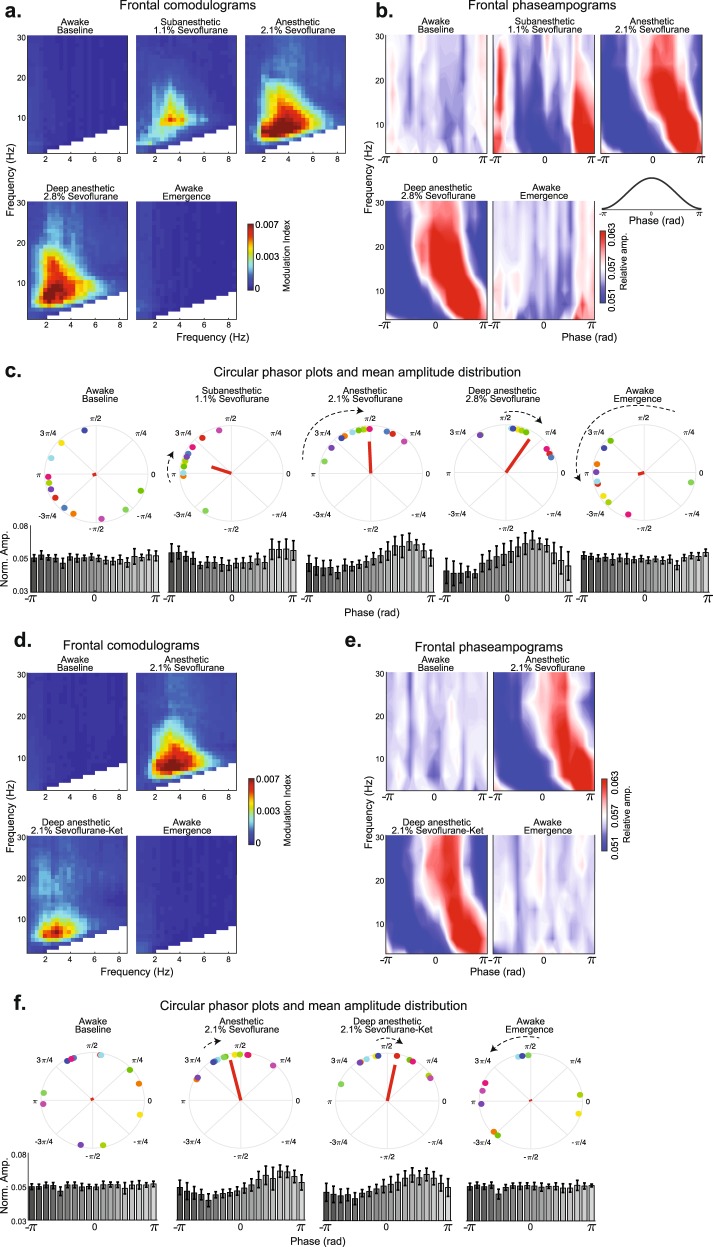
Fig. 4.
Phase-amplitude coupling dynamics associated with sevoflurane-induced anesthetic states. a Frontal comodulograms demonstrated that delta oscillations modulated higher frequencies during sevoflurane-induced anesthetic states. b Frontal phaseampograms between delta and higher frequencies demonstrated that distinct patterns of phase limited neural activity are associated with subanesthetic and anesthetic states. c Frontal circular phasor plots demonstrated that neural activity systematically shifted from π towards 0 phase of delta oscillations as a function of anesthetic depth. The median amplitude vector (red line) was increased from baseline during the anesthetic states. Mean amplitude distribution was not uniformly distributed during sevoflurane-induced anesthetic states. d Frontal comodulograms demonstrated that delta oscillations modulated higher frequencies during the sevoflurane-plus-ketamine induced anesthetic state. e Frontal phaseampograms between delta and higher frequencies demonstrated that the distinct patterns of phase limited neural activity associated with the sevoflurane general anesthetic state were conserved during the sevoflurane-plus-ketamine anesthetic state. f Frontal circular phasor plots also demonstrated that neural activity systematically shifted from π towards 0 phase of delta oscillations as a function of anesthetic depth. The median amplitude vector (red line) was increased from baseline during the anesthetic states. Mean amplitude distribution was not uniformly distributed during sevoflurane-induced anesthetic states. Colored circular dots on phasor plots represent subject level data. Error bars represent standard deviation