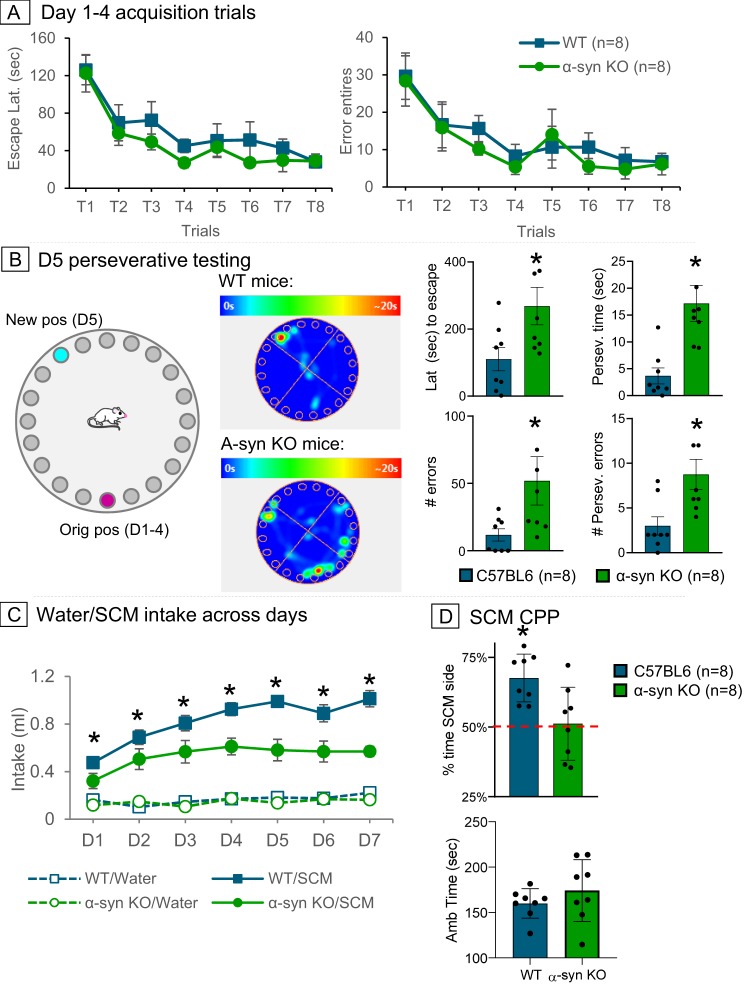
Fig. 2.
a α-Syn KO (green) and WT (blue) mice show similar latencies to find the escape hole and number of errors made during acquisition of the Barnes Maze spatial memory task. b Schematic drawing of the Barnes Maze with the original escape hole position at 6 o’clock (magenta) and changed position (teal) at ~11 o’clock for perseverative testing. Heat map images of mouse location during D5 perseverative testing showing that α-syn KO mice spent more time near the original escape hole position than WT mice. Bar graphs showing that α-syn KO mice took longer to find the newly positioned escape hole, had more general and perseverative errors, and spent more time in the quadrant with the original escape hole position than WT mice. c During the conditioning trials (D1–7), α-syn KO and WT mice ingested more SCM (solid lines) than water (dashed lines), but to a lesser extent by the α-syn KO mice. In addition, α-syn KO mice did not show conditioned preference to SCM; *p < 0.05, SCM = sweetened condensed milk