Fig. 4.
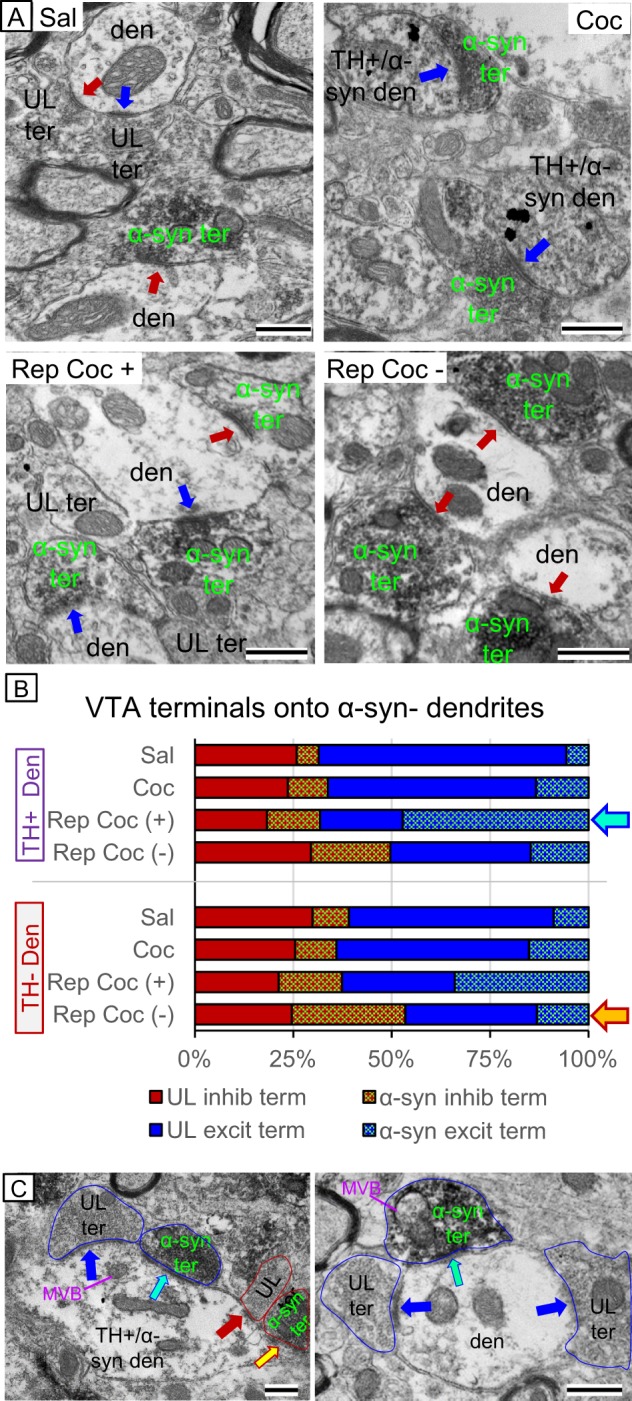
a Electron micrographs showing axon terminals containing α-syn peroxidase immunolabeling (green labels) making excitatory (blue arrows) and inhibitory (red arrows) contacts onto VTA dendrites. b Quantification of characterized synaptic contacts onto TH+ and TH− dendrites in the VTA showing that when systemically present, repeated cocaine (rep coc+) increased α-syn immunolabeling in axon terminals making excitatory-type synaptic contacts onto dopamine dendrites (teal arrow). When cocaine or its metabolites were no longer systemically present (rep coc−), α-syn immunolabeling was increased in axon terminals making inhibitory-type synaptic contacts onto non-dopaminergic dendrites in the VTA (yellow arrow). c Electron micrographs showing the selectivity of α-syn immunolabeling. Axon terminals with (teal arrows) and without (blue arrows) α-syn immunolabeling can be seen making excitatory-type synaptic contacts onto the same dopamine (TH+) or non-dopamine dendrite within the VTA. Similarly, axon terminals with (yellow arrow) or without (red arrow) α-syn labeling can be seen making inhibitory contacts onto the same dopamine dendrite. Scale bar = 500 nm; den = dendrite; ter = axon terminal; UL = unlabeled
