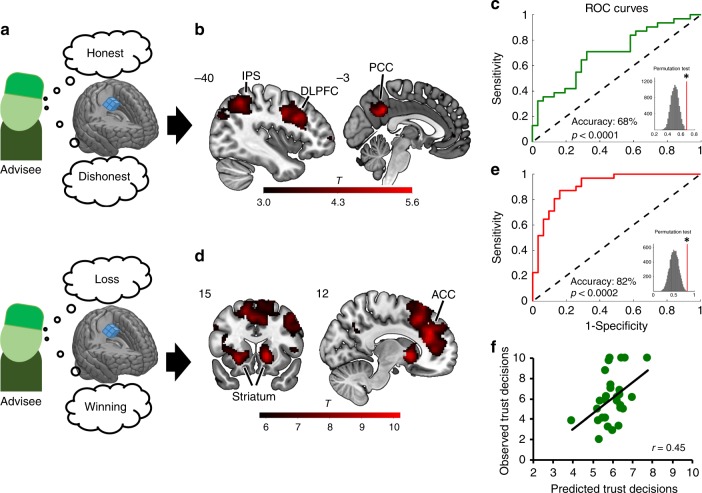
Fig. 3.
Decoding honesty and predicting trust. In two MVPAs applied to the feedback phase of the TAG (a), a support vector machine (SVM) was trained to decode honest and dishonest advice (GLM1) to determine the trustworthiness decoding network (upper), and to decode winnings and losses (GLM2) to determine the value decoding network (lower). The trustworthiness decoding network (b) included brain regions such as the PCC, DLPFC, and IPS, and could successfully distinguish neural signatures of honesty and dishonesty in out-of-sample individuals (c). The value decoding network (d) included the striatum and ACC and could successfully distinguish neural signatures of winnings and losses in out-of-sample individuals (e). Finally, a multivariate prediction analysis with support vector regression (SVR) showed that the neural patterns of the trustworthiness decoding network successfully predicted individual economic trust decisions in the TG, thereby showing across-context generalizability (f). Both out-of-sample classification and prediction analyses were based on a leave-one-subject-out cross-validation procedure and their significance tested using a permutation test with 10,000 permutations. Each dot represents one participant. See also Supplementary Fig. 2 and Supplementary Table 1. MVPA, multivariate voxel pattern analysis; TAG, take advice game; PCC, posterior cingulate cortex; IPS, intraparietal sulcus; DLPFC, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; ACC, anterior cingulate cortex; TG, trust game. Heatmap represents t values