Fig. 5.
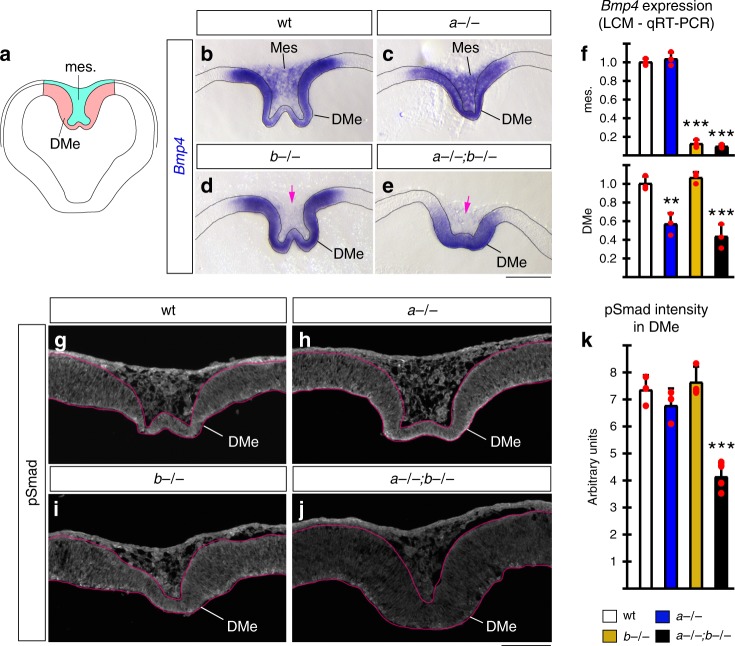
Lmx1a and Lmx1b regulate Bmp signaling by controlling expression of Bmp4. a Schematic of e10.5 coronal telencephalic section showing DMe (red) and medial mesenchyme (green). b–e High magnification images of dorsal midline region of e10.5 telencephalic coronal sections stained with Bmp4 in situ probe. (Low magnification images of the same sections are shown in Supplementary Fig. 14.) b In wild-type telencephalon, Bmp4 was expressed in the DMe and medial mesenchyme adjacent to DMe (mes.). c–e Loss of Lmx1b abolished Bmp4 expression in medial mesenchyme (pink arrows in d, e) but not DMe. Based on in situ, loss of Lmx1a did not obviously reduce Bmp4 expression. f qRT-PCR analysis of DMe (red region in panel a) and medial mesenchyme (green region in panel a) isolated by laser capture microdissection (LCM). Based on qRT-PCR, loss of Lmx1b reduced expression of Bmp4 in medial mesenchyme (mes.) (***p < 0.001 for Lmx1b−/− versus wild type and Lmx1a−/−;b−/− versus wild-type comparisons, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test, n = 3 embryos per genotype). Loss of Lmx1a reduced expression of Bmp4 in the DMe (**p < 0.01 for Lmx1a−/− versus wild type and ***p = 0.001 for Lmx1a−/−;b−/− versus wild-type comparisons, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test, n = 3 embryos per genotype). g–j pSmad immunohistochemistry on e10.5 coronal sections. Only simultaneous, but not individual loss of Lmx1a and 1b significantly reduced pSmad intensity in the DMe (***p ≤ 0.001 for Lmx1a−/−;b−/− versus wild type, Lmx1a−/−;b−/− versus Lmx1a−/−, and Lmx1a−/−;b−/− versus Lmx1b−/− comparisons, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test, n = 3 wild-type embryos, n = 3 Lmx1a−/− embryos, n = 3 Lmx1b−/− embryos, and n = 4 Lmx1a−/−;b−/− embryos). All data are mean ± s.d. Source data for panels f, k are provided as Source Data File. Scale bars: 200 μm (b–e); 100 μm (g–j)