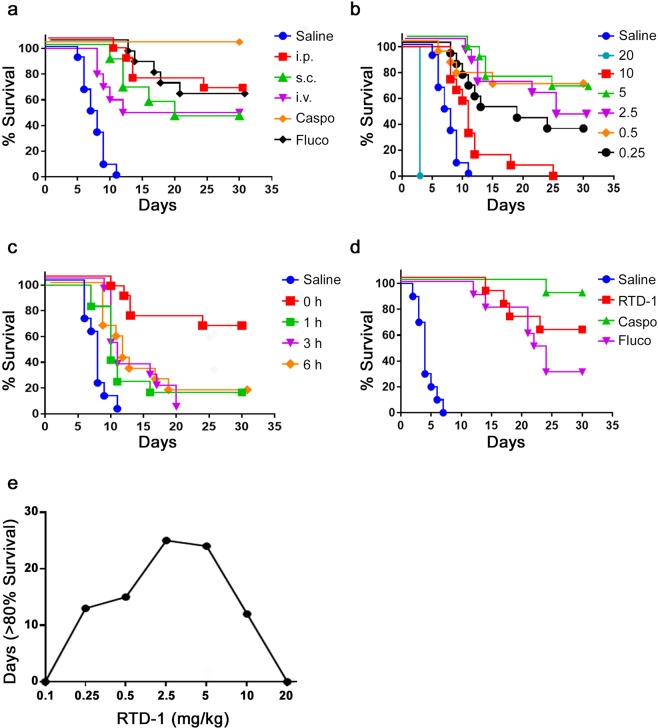
Figure 3.
RTD-1 promotes survival of mice with disseminated C. albicans infection. (a) RTD-1 efficacy is independent of route of peptide administration. Mice infected i.v. with 3 × 105 C. albicans SC5314 were treated once at T = 0 with 5 mg/kg RTD-1 administered i.p. (n = 13), i.v. (n = 12), or s.c. (n = 12). Cohorts receiving fluconazole (Fluco; n = 12) or caspofungin (Caspo; n = 12) were treated once, 5 mg/kg, by i.p. injection at T = 0. Controls received saline (n = 12) i.p at T = 0, and mice were monitored for 30 days. Relative to saline controls, RTD-1 treated mice had increased survival (P = 3.3 × 10−7, i.p.; P = 1.5 × 10−5, s.c.; P = 6.9 × 10−4, i.v.) as did Caspo and Fluco treated animals (P = 4.3 × 10−7). There was no statistical difference observed among groups treated with RTD-1, or between RTD-1 and Fluco, whereas Caspo was significantly more effective than RTD-1 or Fluco (see Suppl. Table 1). (b) Dose dependent efficacy of RTD-1. Mice (n = 12 or 13 for each cohort) were infected i.v. with SC5314 (as in panel a) and treated with a single i.p. dose (mg/kg shown) of RTD-1 at T = 0 and monitored for 30 d. RTD-1 significantly enhanced survival (P < 0.00001 for all treatment cohorts but the 10 mg/kg cohort for which P = 0.0013, and the 20 mg/kg for which RTD-1 significantly accelerates death, P = 6.3 × 10−5; see Suppl. Table 1 for statistical summary). (c) Effect of infection-treatment interval on single dose RTD-1 efficacy. Mice were infected i.v. (as in panel a) and treated i.p. with 5 mg/kg RTD-1 at intervals following infection: T = 0 (n = 13, data redrawn from Fig. panel a), 1 h (n = 12), 3 h (n = 12), and 6 h (n = 12). Saline (control) vehicle was administered i.p. at T = 0 and all mice were monitored for up to 30 days. While peptide treatment enhanced survival compared to saline control (P < 0.002 for all peptide treated cohort; Suppl. Table 1), delaying treatment reduced single dose efficacy of RTD-1. (d) Multiple RTD-1 dosing is effective in delayed treatment of systemic candidiasis. Mice (n = 10 for each group) were infected i.v. with C. albicans SC5314. Beginning 24 h p.i., mice received daily i.p. injections of 5 mg/kg of RTD-1, 5 mg/kg Fluco, 5 mg/kg Caspo, or saline for 7 days and mice were monitored for up to 30 d. All three agents markedly improved survival (P = 3.4 × 10−6) compared to saline treatment. Efficacy of RTD-1 was not statistically different than that of Fluco or Caspo, but Caspo was superior to Fluco (P = 4.7 × 10−3, Suppl. Table 1). (e) Inverted “U” effects of RTD-1 treatment of systemic candidiasis. Survival rates from Fig. 3b and RTD-1 0.1 mg/kg (not shown) are plotted as number of days showing >80% survival in function of RTD-1 concentration ranging from 0.1 to 20 mg/kg. RTD-1 enhanced survival as dose levels are increased up to 5 mg/kg, but decreased in efficacy with dosing at 10 and 20 mg/kg, resembles an inverted “U” shape.