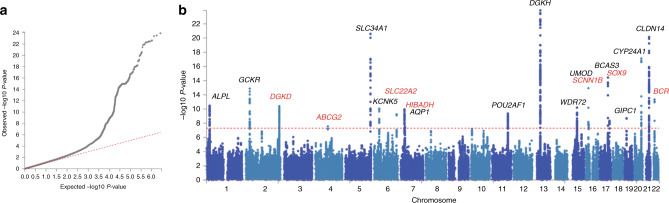
Fig. 1.
Results of trans-ethnic genome-wide association study in kidney stone disease. A trans-ethnic meta-analysis of kidney stone disease was performed for 12,123 individuals with kidney stone disease and 417,378 controls from the UK Biobank and BioBank Japan. a is a quantile-quantile plot of observed vs. expected p-values. The λGC demonstrated some inflation (1.0957), but the LD score regression (LDSC) intercept of 0.9997, with an attenuation ratio of 0.0075 indicated that the inflation was largely due to polygenicity and the large sample size. b is a Manhattan plot showing the genome-wide p values (-log10) plotted against their respective positions on each of the autosomes. The horizontal red line shows the genome-wide significance threshold of 5.0 × 10−8. Loci have been labeled with the primary candidate gene at each locus, as shown in Table 1. Previously unreported GWAS-discovered kidney stone loci are highlighted in red