Figure 2.
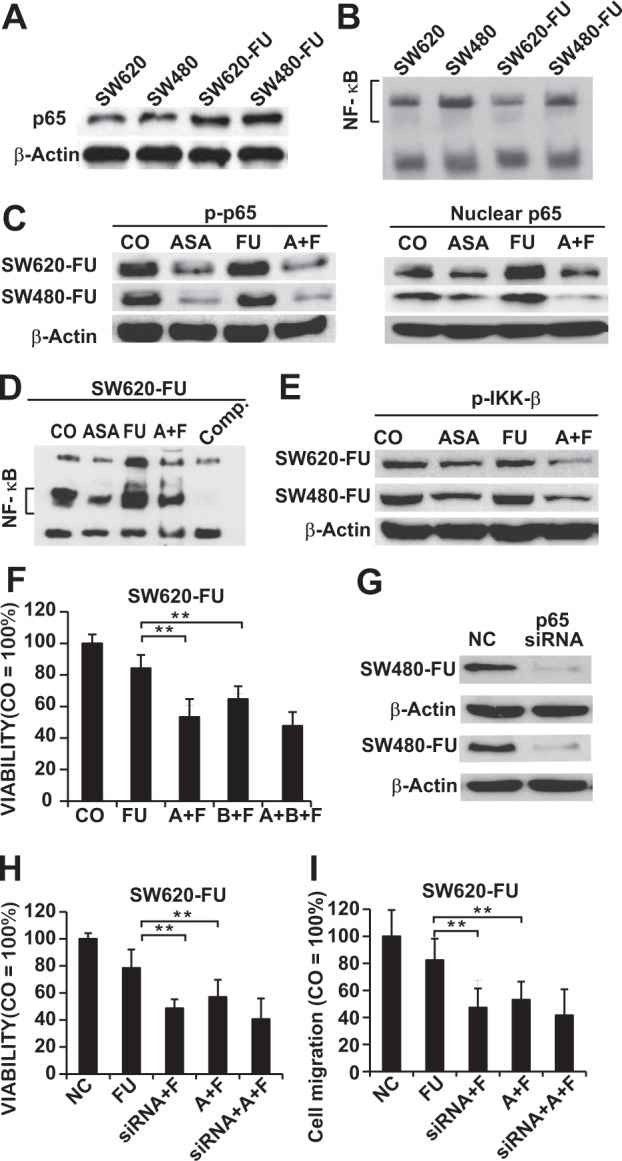
Aspirin enhances the anti-tumor effect of 5-FU by inhibiting the 5-Fu-induced abnormal NF-κB abnormal in resistant CRC cells. (A) Nuclear protein was extracted and the basic expression levels of p65 in SW620, SW480, SW620-FU and SW480-FU were determined by Western blotting analysis. (B) NF-κB was detected by DNA binding in SW620, SW480, SW620-FU, and SW480-FU through the electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). (C) SW620-FU and SW480-FU cells were treated with 2.5 mM ASA, 150 μM (FU), or both of the two drugs (A + F), respectively, and the expression of nuclear p65 and p-p65 was measured at 48 h through Western blotting analysis. β-Actin serves as a control. (D) The NF-κB activity in SW620-FU cells is analyzed by EMSA after 6 h of treatment as described above. Comp: a 10-fold excess of unlabeled oligonucleotide is added to the untreated cells for control DNA-binding reaction, followed by incubation with the biotin-labeled oligonucleotide probe for NF-κB. (E) The expression of IKK-β was measured at 48 h through Western blotting analysis as described above. (F) SW620-FU cells were treated with 150 μM FU alone, the double combination of 2.5 mM ASA plus 150 μM FU(A + F) or 10 μM Bay11-7082 (A + B), or triple agents combination (A + B + F), respectively, and the cellular viability was measured 72 h later with an MTT assay. (G) Western blotting was conducted 48 h after treatment with nonspecific control siRNA (NC) or p65 siRNA. (H) Cells were transfected with p65 siRNA for 24 h. Then, cells treated with 5-FU or aspirin or both agents together for another 72 h and the viability of cells were detected with MTT. (I)The indicated cells transfected with or without p65-siRNA for 24 h were treated with 5-FU or aspirin or both agents together for 24 hours, and the invasion cells were evaluated using the Transwell chambers coated with Matrigel.
