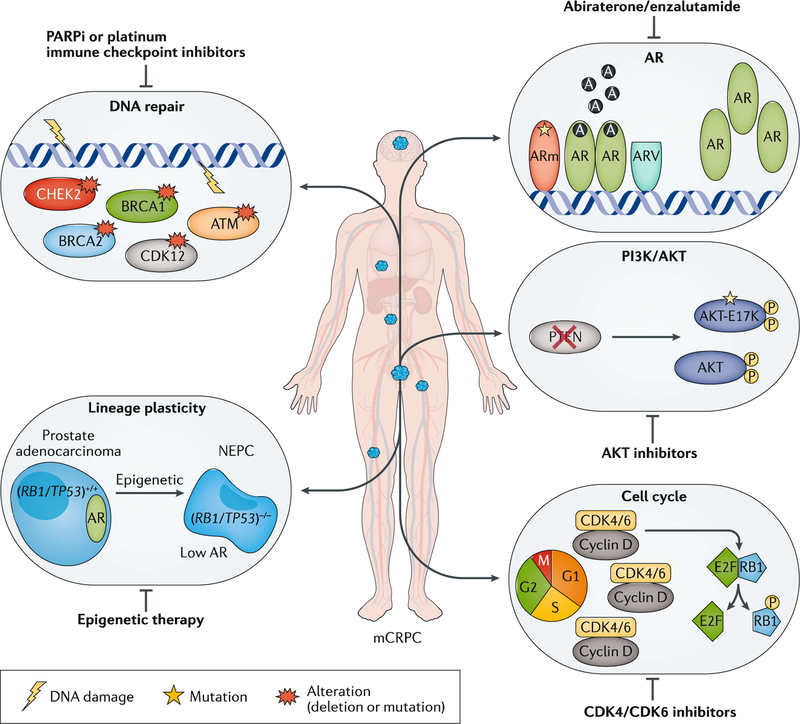
Fig. 1 |. Precision medicine in mCRPC.
Genomic alterations are often heterogeneous across patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). Different alterations can have distinct biological roles in driving mCRPC progression and response, and resistance to therapies. By understanding each altered gene or pathway in an individual, precision medicine has the potential to guide unique therapeutic approaches for patients and improve clinical outcomes. A, androgen; AR, androgen receptor; ARm, mutant AR; ARV, AR splice variant; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; NEPC, neuroendocrine prostate cancer.