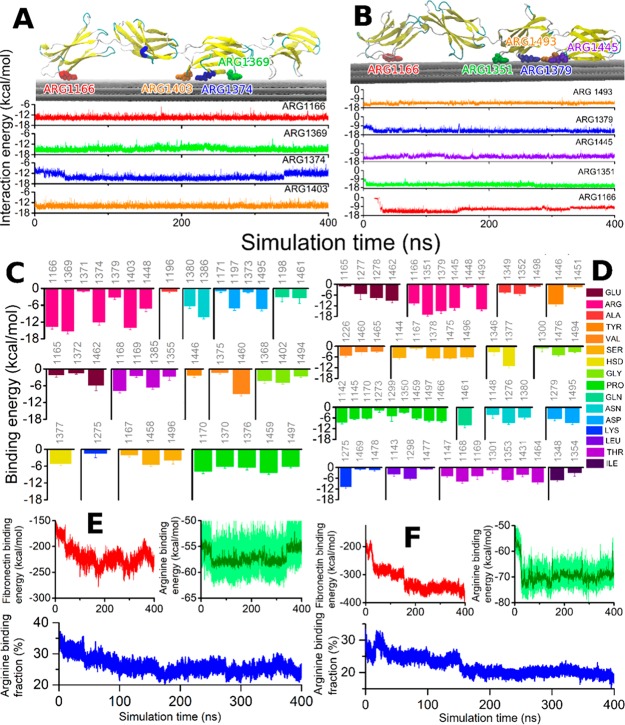
Figure 2.
Fibronectin interaction with graphene is stabilized by arginine residues. (A) Graphical rendering of the stabilized fibronectin atop the three graphene sheets with the four best arginine binders highlighted (Arg1166, Arg1369, Arg1374, Arg1403). The time evolution of the binding energy of these arginine residues with graphene is shown in the lower panel, color-coded for the amino acid residues. (B) Analogous to A but showing the data for the second studied configuration. This configuration features five arginine residue binders (Arg1166, Arg1351, Arg1379, Arg1445, Arg1493). (C) Binding energy with graphene computed for every amino acid with average binding energy above 1 kcal/mol, averaged over the 400 ns simulation. (D) Analogous to C, for the second studied configuration. The residue numbers are indicated, while the corresponding amino acid types are color-coded for both panels (C and D). (E and F) Time evolution of the fibronectin and arginine interaction energy with graphene for the two configurations. The lower plots in both panels show the fraction of arginine residue binding energy with respect to the total fibronectin-binding energy as a function of simulation time.