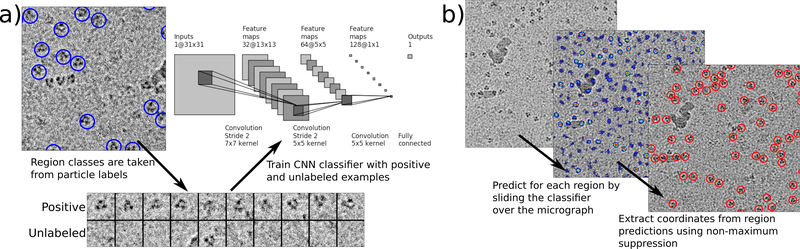
Figure 1 |.
Topaz particle picking pipeline using CNNs trained with positive and unlabeled data. (a) Given a set of labeled particles, a CNN is trained to classify positive and negative regions using particle locations as positive regions and all other regions as unlabeled. Labeled particles from EMPIAR-10096 are indicated by blue circles and a few positive and unlabeled regions are depicted. (b) Once the CNN classifier is trained, particles are predicted in two steps. First, the classifier is applied to each micrograph region to give per region predictions. Second, coordinates are extracted from the region predictions using non-maximum suppression. The left image shows a raw micrograph from EMPIAR-10096. The middle image depicts the micrograph with overlaid region predictions [blue = low confidence, red = high confidence]. The right image indicates predicted particles after using non-maximum suppression on the region predictions.